Introduction to Image Analysis with Fiji
Peter Sobolewski (he/him)
Systems Analyst, Imaging Applications - Research IT
Use to advance the slide
Thanks to:
- Erick Ratamero (JAX), who prepared the original of these materials
- Dave Mason, (formerly) from the University of Liverpool, who prepared the original materials Erick adapted
- Unfortunately Dave's original slides are lost to time, but they looked very much like these.
- These slides: https://thejacksonlaboratory.github.io/fiji_workshops/IntroFiji.html
- The JAX Fiji workshops landing page: https://thejacksonlaboratory.github.io/fiji_workshops/
- Navigation: arrow keys left and right to navigate
- `m` key to get to navigation menu—browser back button won't work between slides
- Escape for slide overview
- Fiji & Bioimage analysis resources:
- Fiji Website
- Fiji Training Manual by Cameron Nowell, Monash University
- Introduction to Bioimage Analysis online book
- Where to find help after the workshop:
- image.sc Forum
- #image-analysis Slack channel
- Imaging Applications Coffee Hour
How an Image is formed
Understanding digital images


Widefield and Confocal microscopes acquire images in different ways.
Widefield and laser-scanning microscopes acquire images in different ways.
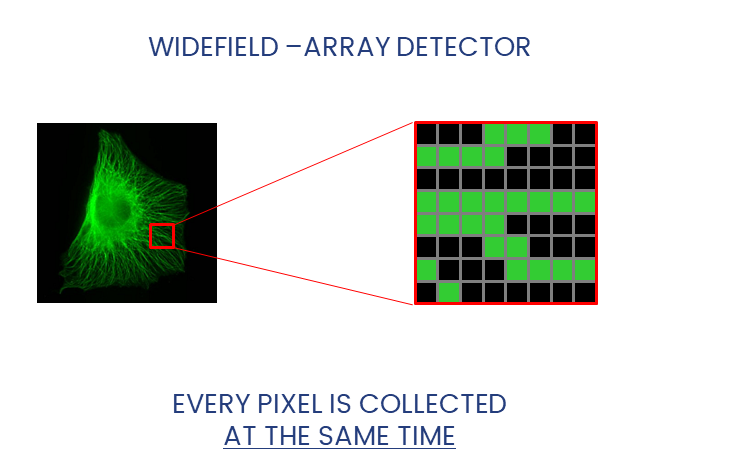
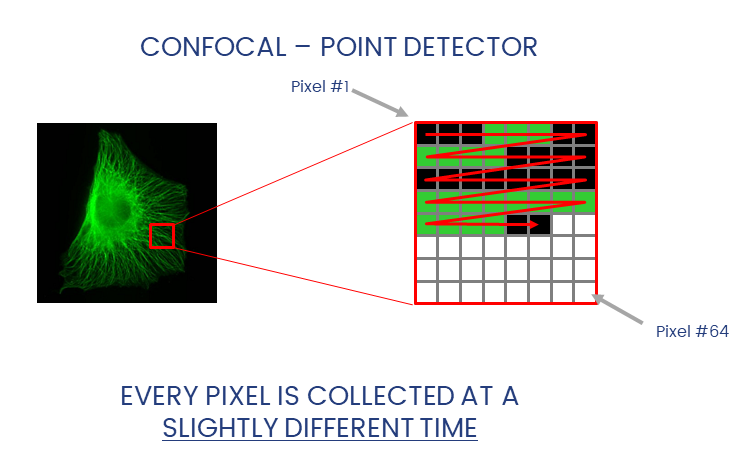
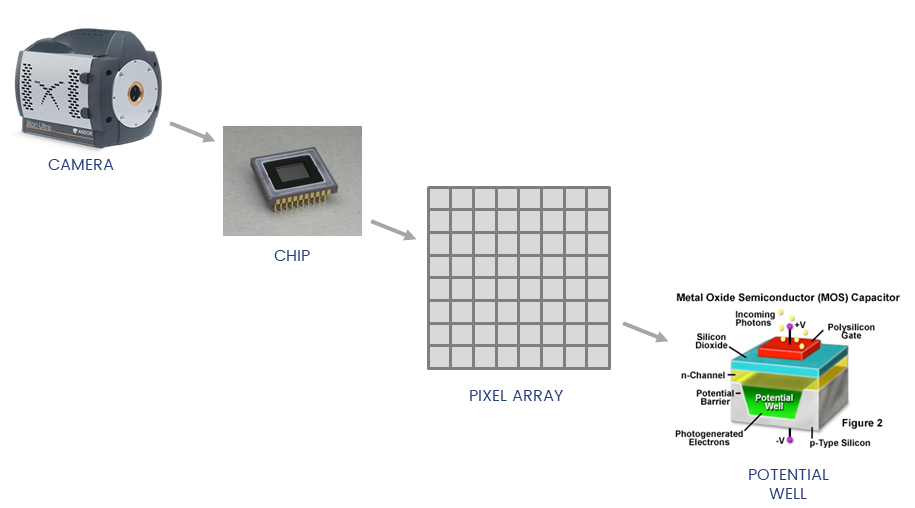
Detectors collect photons and convert them to a voltage
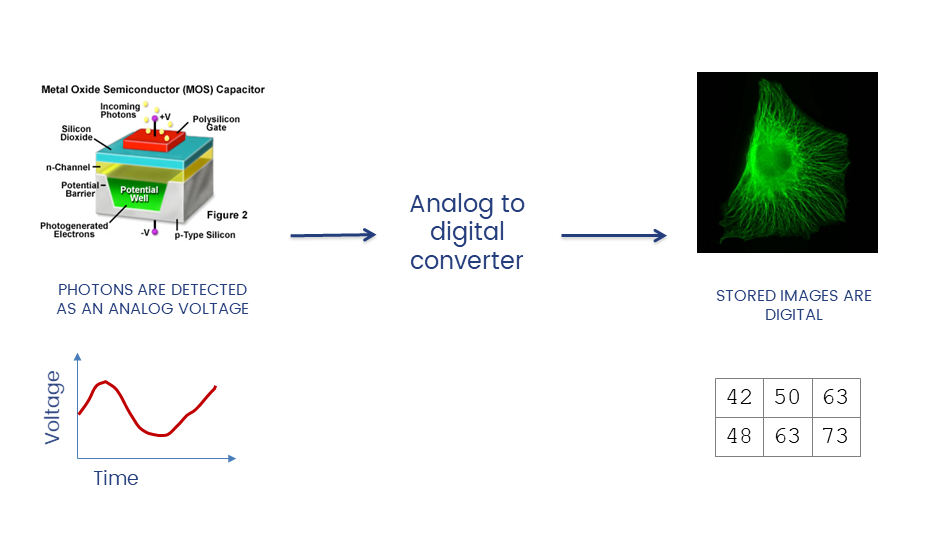
The A/D converter determines the dynamic range of the data

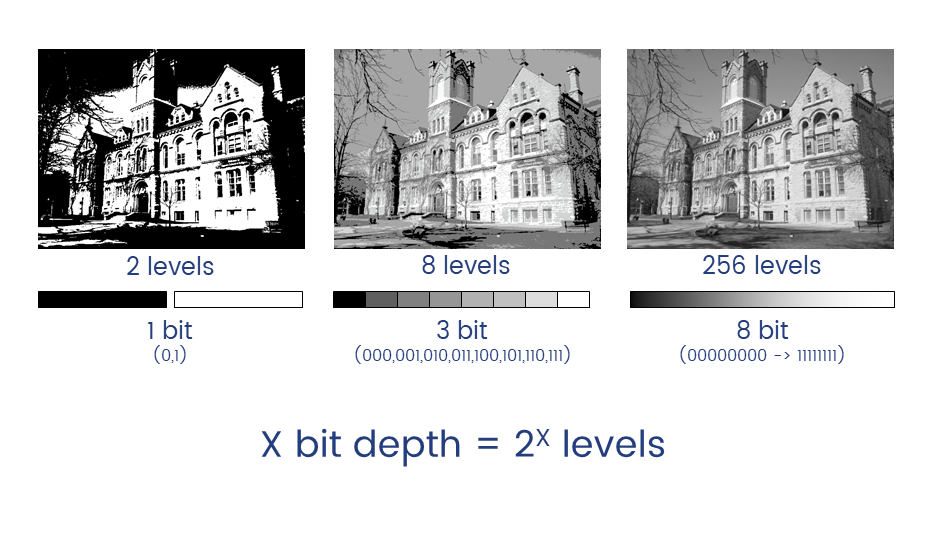
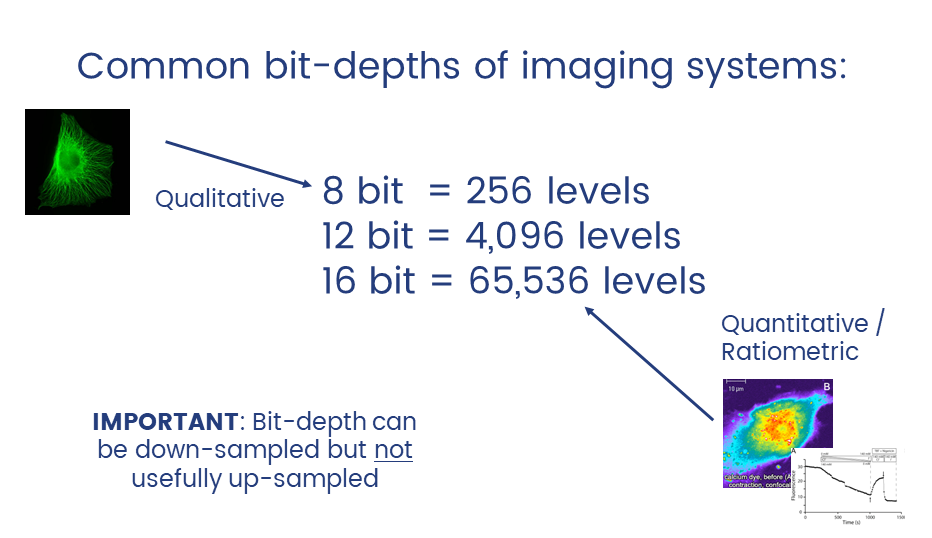
Unless you have good reason not to, always collect data at the highest possible bit depth

32 bit is a special data type called floating point.
TL;DR: pixels can have non-integer values which can be useful in applications like ratiometric imaging.
Introduction to ImageJ & Fiji
A cross platform, open source, Java-based image processing program

ImageJ is a java program for image processing and analysis.
Fiji extends this via plugins.
- Open Source (free to modify)
- Extensible (plugins)
- Cross-Platform (Java-Based)
- Scriptable for Automation
- Vast Functionality
- Includes the Bioformats Library

Learn more about Bio-Formats here
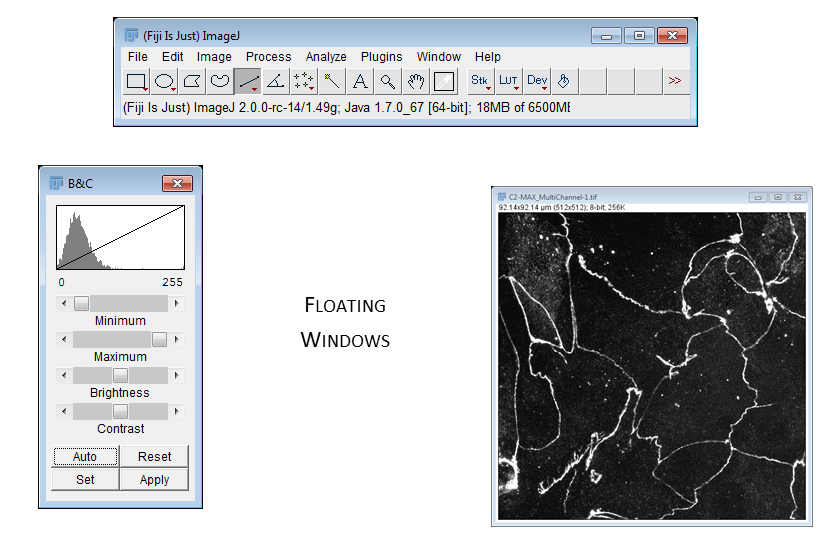
A few small productivity tips
- Zoom using +/- keys
- When zoomed in, pan by holding space and click-dragging with mouse
- Hit 'Enter' to bring the Fiji window to the front
- Press 'L' to access the search/command palette
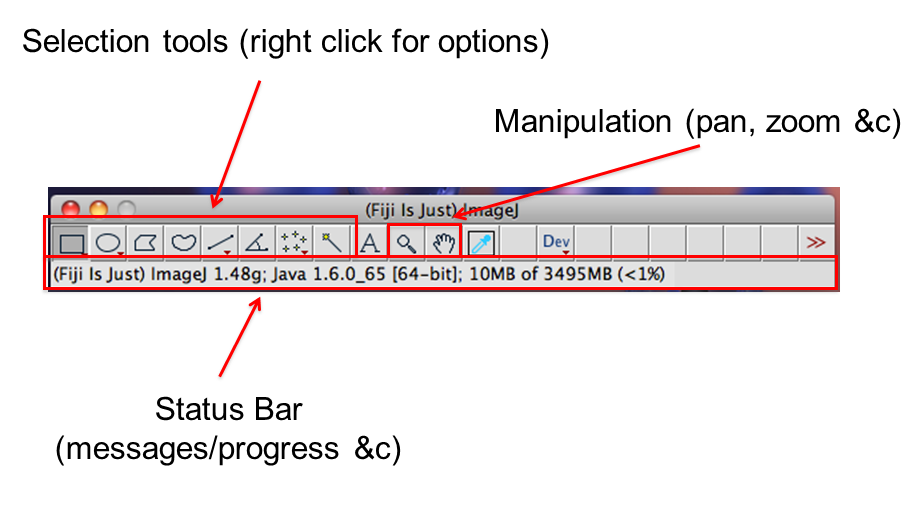
[Window > Tile]command is very useful when opening multiple images- infobar (right top): gives info on the image
- statusbar (right bottom): gives current cursor coordinates and intensity readout
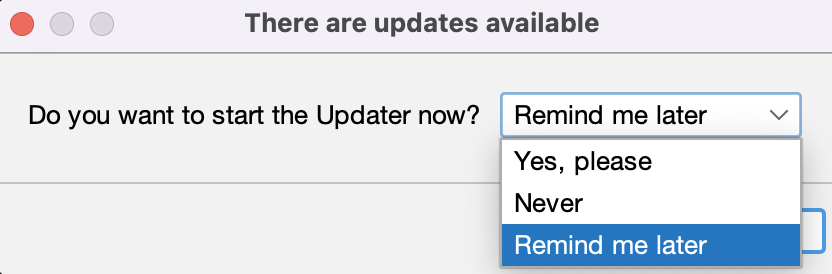
A word about updating
- Fiji includes a built-in updater mechanism, which may prompt you at launch:
- You can access it using
[Help > Update...] - This will also update installed plugins
- In the middle of a project, best to be conservative and not update—barring bugs
- Note: you can duplicate your Fiji and have a backup!
Hands on With Fiji
Getting to know the interface, info & status bars, calibrated vs non-calibrated images
Exercises will be provided in-line, as links to PDFs—right-click and open in a new tab
Commands on the Fiji menu will look like: [File > Save]
Sample/exercise data will look like this: 01-Photo.tif
Right-click to copy the URL and use [File > Import > URL...] to open
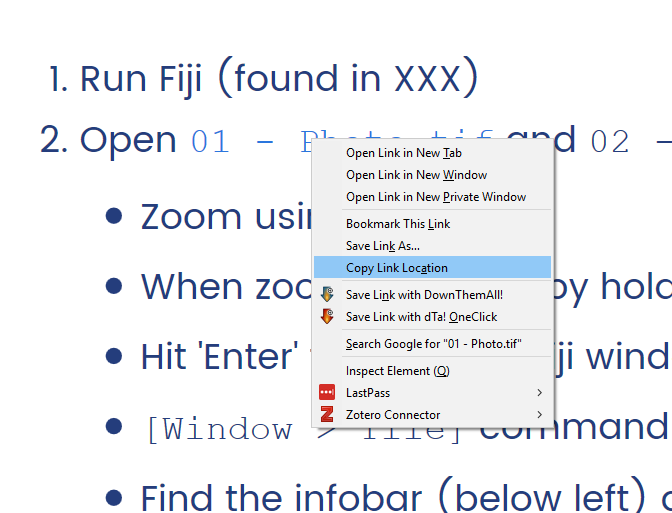
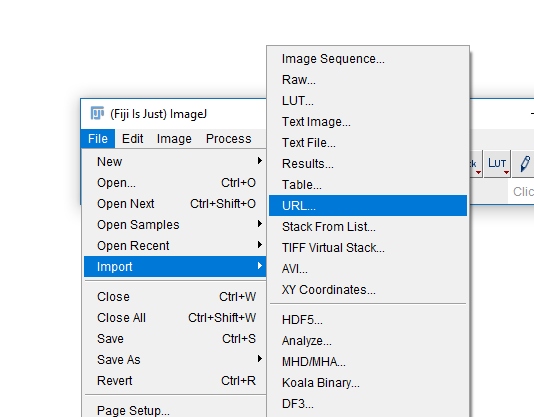
(Paste in the URL in the resulting box)
Exercise 1
- Open
Task1.pdfand follow the instructions there. - You will need these two images:
01-Photo.tifand02-Biological_Image.tif
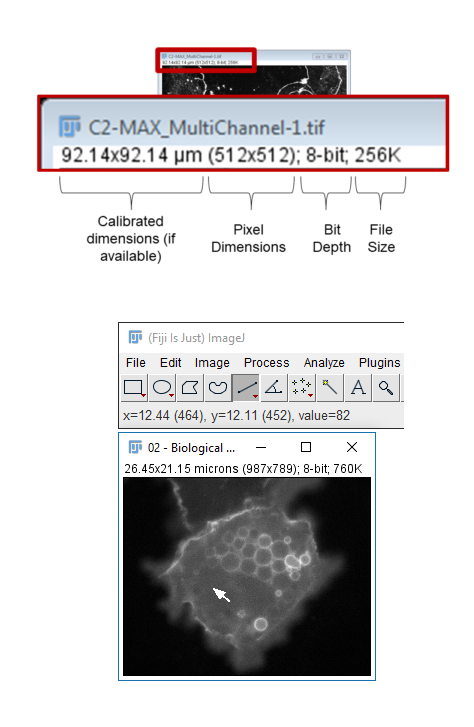
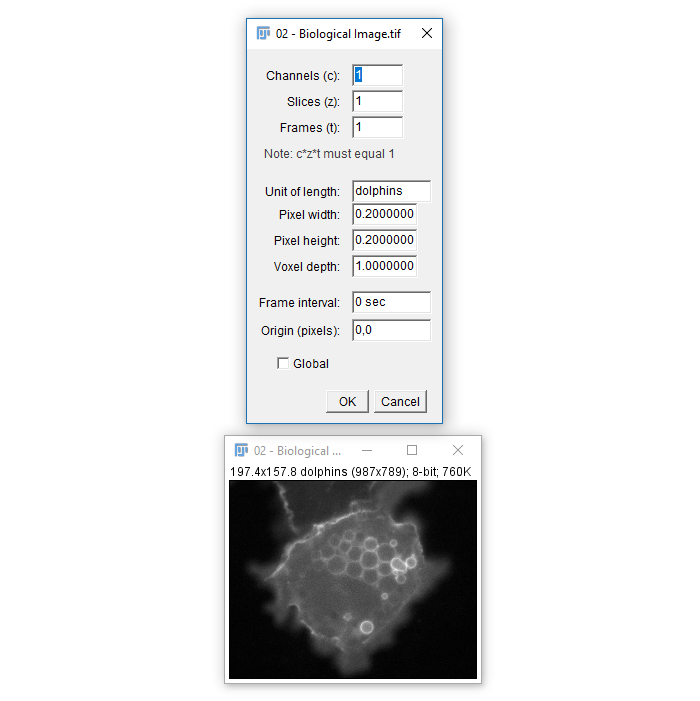
Calibration
- The Infobar is a great way to tell if your image is calibrated
- Running
[Image > Properties]also allows you to view and set calibration - The spatial calibration can be in any unit you like but (almost) all subsequent measurements will use that unit!
- For μm, use
umormicron - Or use whatever domain specific unit, even
dolphins
Basic Manipulations
Intensity and Geometric adjustments
Images are an array of intensity values. The intensity histogram shows the number (on the y-axis) of each intensity value (on the x-axis) and thus the distribution of intensities
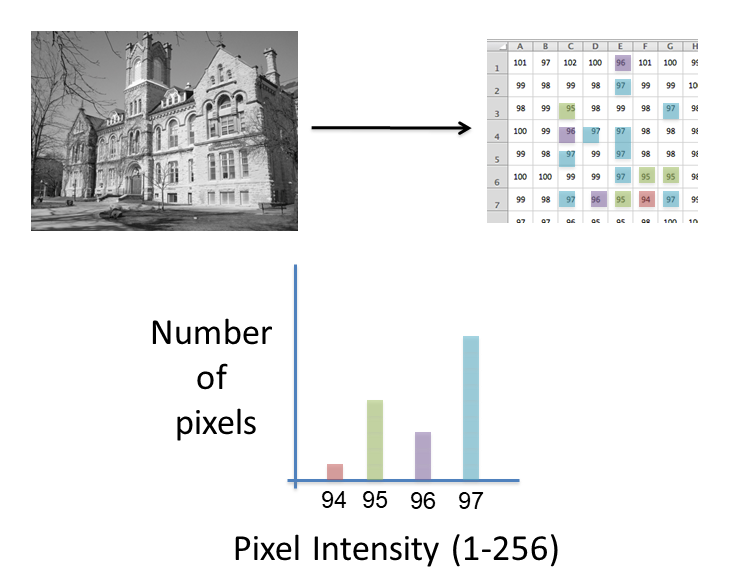
Photos typically have a broad range of intensity values and so the distribution of intensities varies greatly
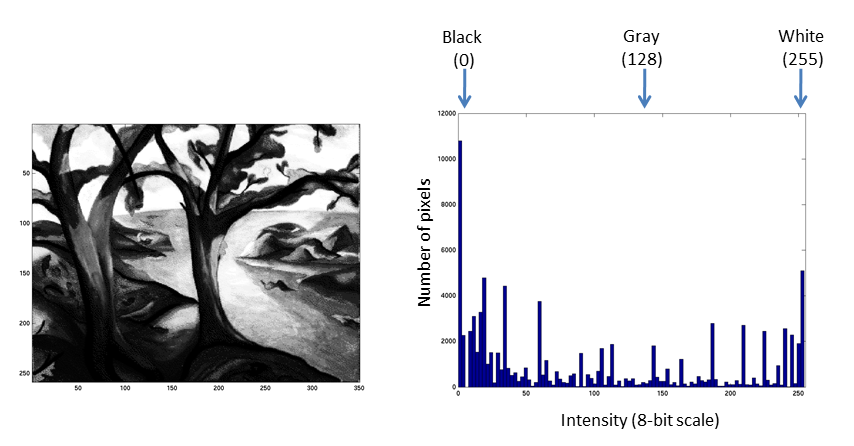
Fluorescent micrographs will typically have a much more predictable distribution:
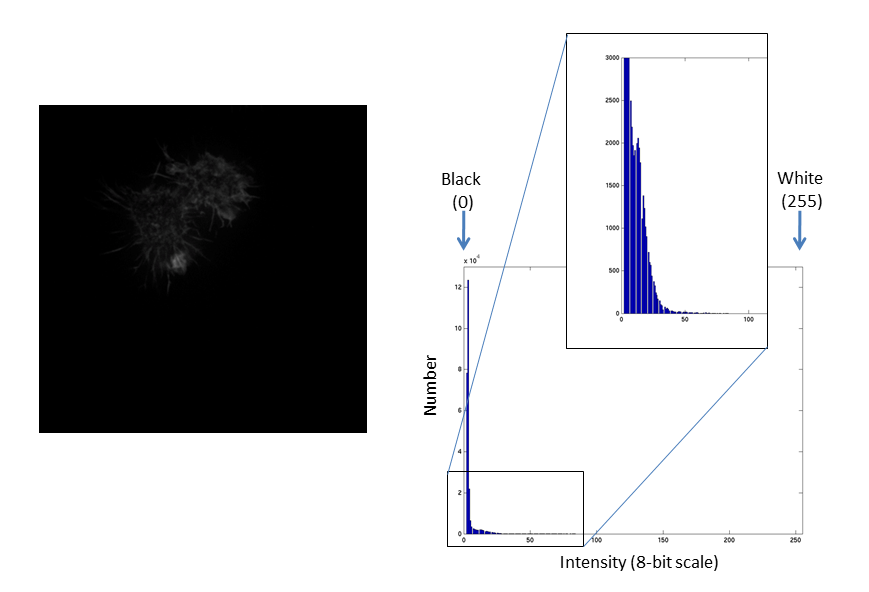
The Black and White points of the histogram dictate the bounds of the display (changing these values alters the brightness and contrast of the image)
They are often called "the contrast limits"
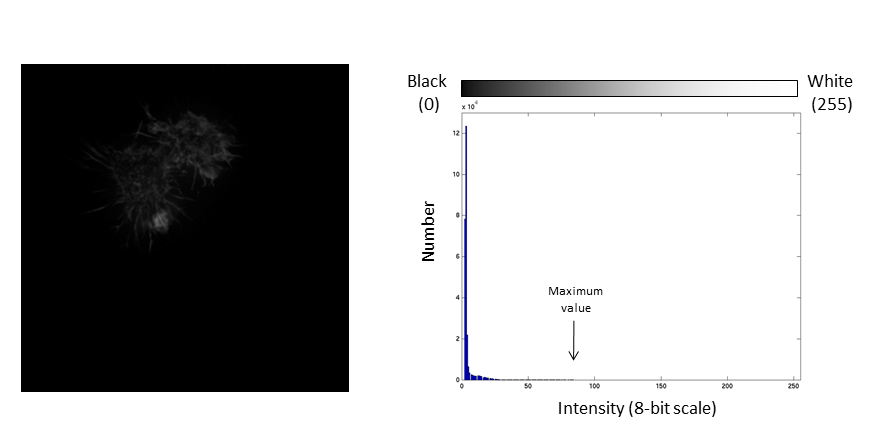
- Brightness: horizontal position of the display window
- Contrast: distance between the black and white point
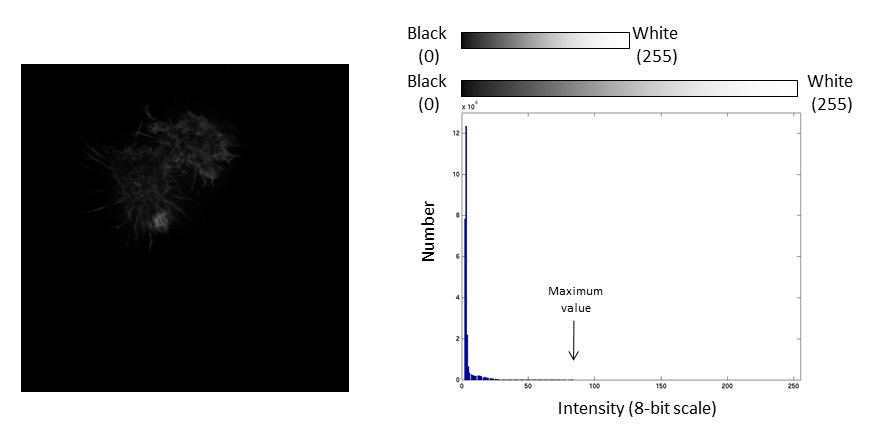
The histogram is now stretched and the intensity value of every pixel is effectively doubled which increases the contrast in the image
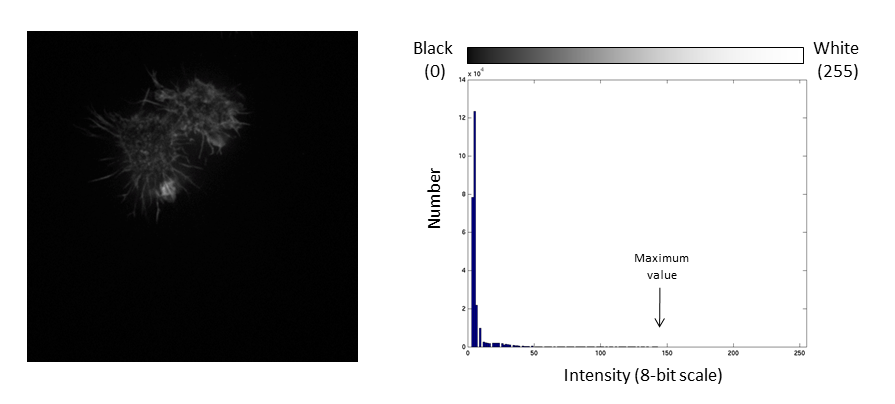
If we repeat the same manipulation, the maximum intensity value in the image is now outside the bounds of the display scale!
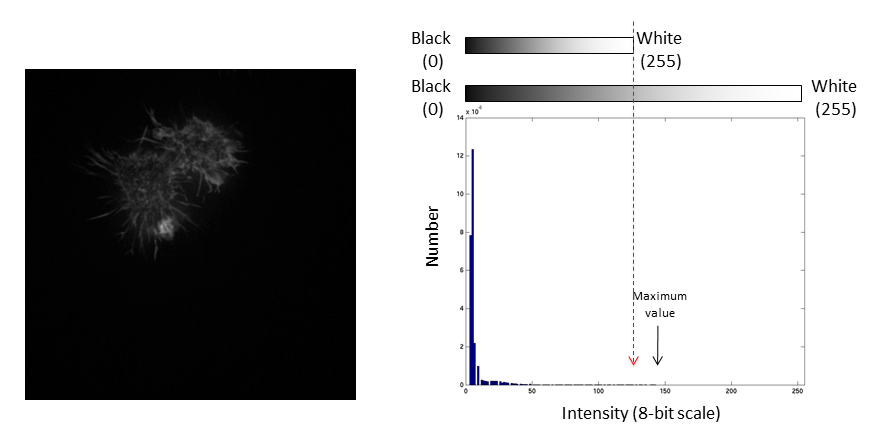
Values falling beyond the new White point are dumped into the top bin of the histogram (IE 256 in an 8-bit image) and information from the image is lost
This is often called "clipping"
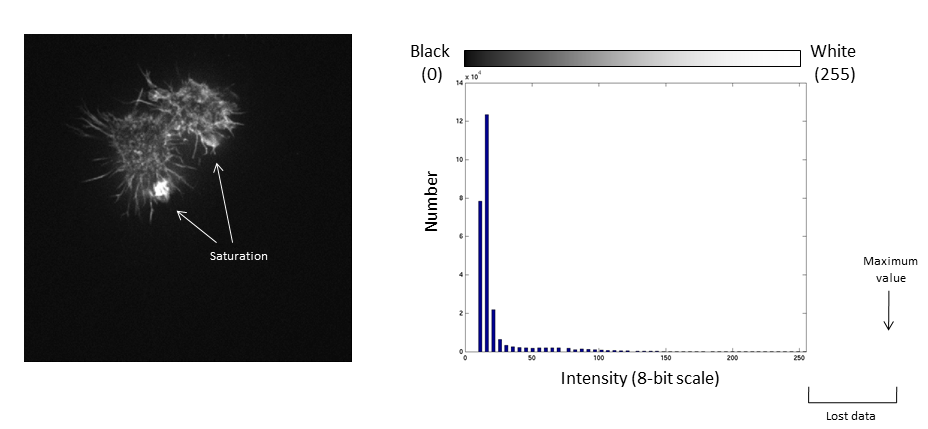
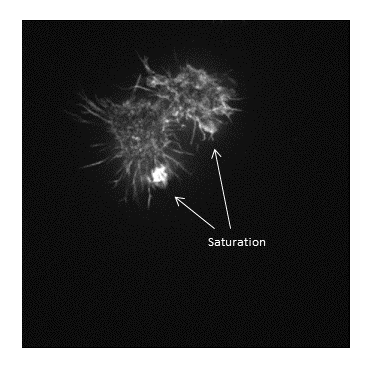
Be careful when applying changes to contrast limits, as they will change the pixel values!
Be warned: removing information from an image is deemed an unacceptable maniplulation and can constitute academic fraud!
For an excellent (if slightly dated) review of permissible image manipulation see:Rossner & Yamada (2004): "What's in a picture? The temptation of image manipulation"
The best advice is to get it right during acquisition and make sure you compare apples to apples
Exercise 2
- Open
Task2.pdfand follow the instructions there. - You will need this image:
02-Biological Image.tif
Measurements and scale bars
Making measurements, what to measure, line vs area, adding a scale bar
[Analyze > Measure] (or `m` keyboard shortcut) is used to make measurements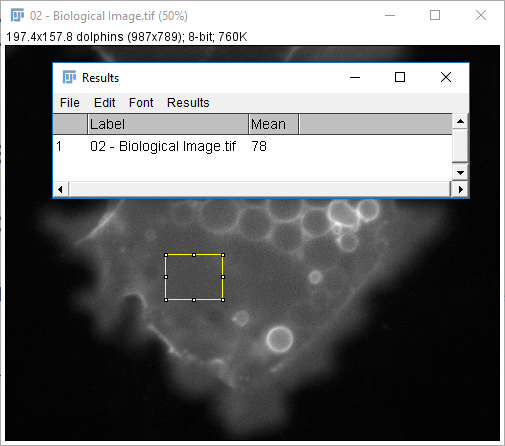
The measurements provided are set via [Analyze > Set Measurements...] except for selection-specific measurements (length, angle, coords)
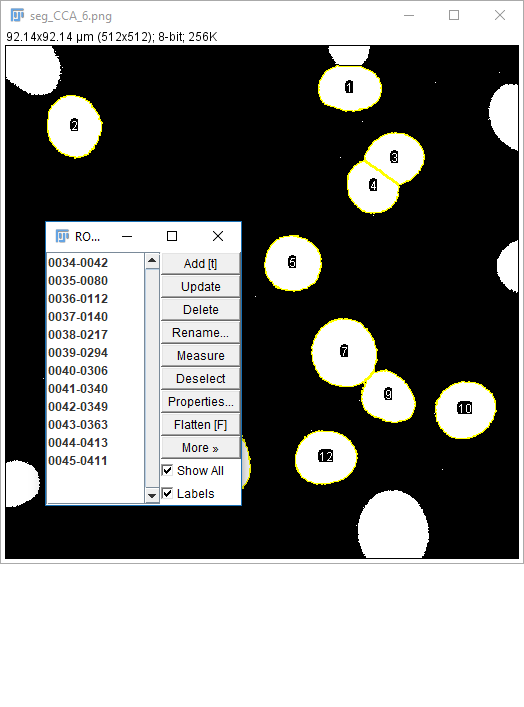
[Analyze > Tools > ROI Manager...]to open the ROI Manager- After making a selection (any type), press `Add` in the ROI Manager or hit 't' or run
[Edit > Selection > Add to Manager] - Repeat as needed for your ROI
- Run
[More > Multi-measure] - Use
[More > Save]for better data provenance!
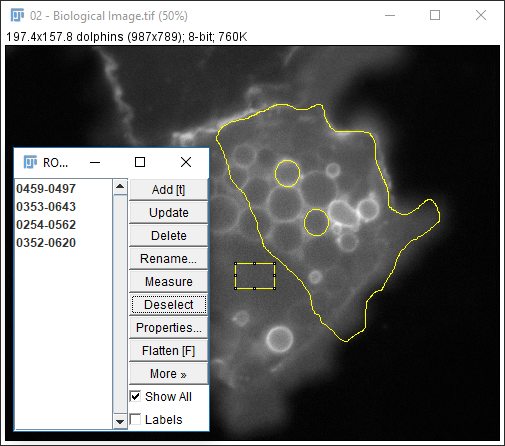
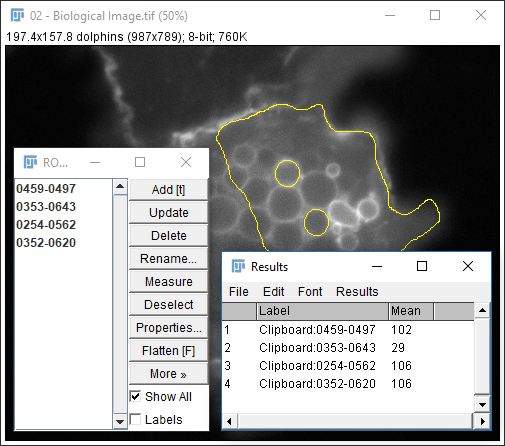
Exercise 3
- Open
Task3.pdfand follow the instructions there. - You will need this image:
02-Biological Image.tif
What if my image is uncalibrated?
- If you know the pixel size, use
[Image > Properties...]
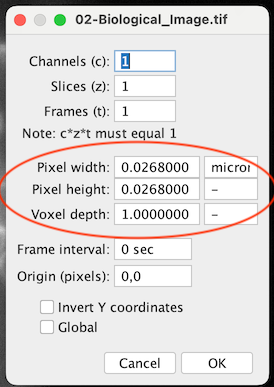
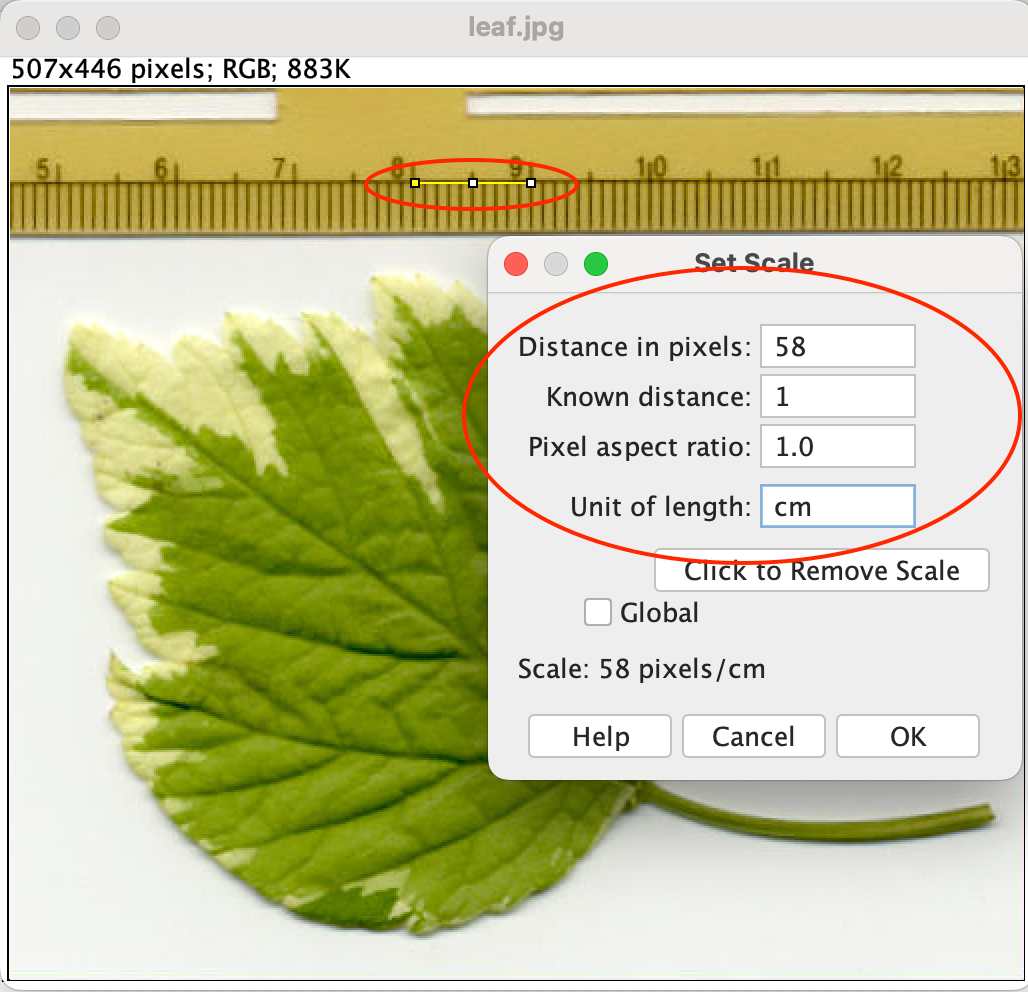
- If you have a reference, mark it with the Line tool and use
[Analyze > Set Scale...]
Stacks
Understanding how Fiji deals with multidimensional images
Some file formats (eg. TIF) can store multiple images in one file which are called stacks
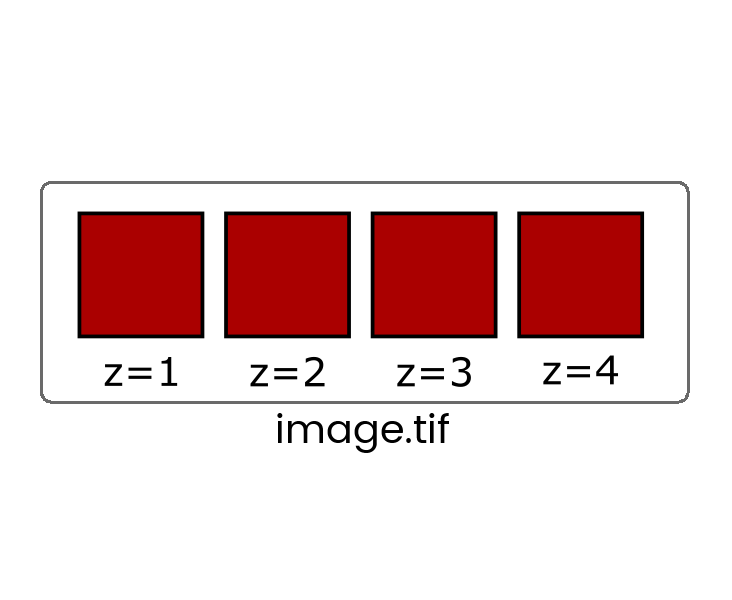
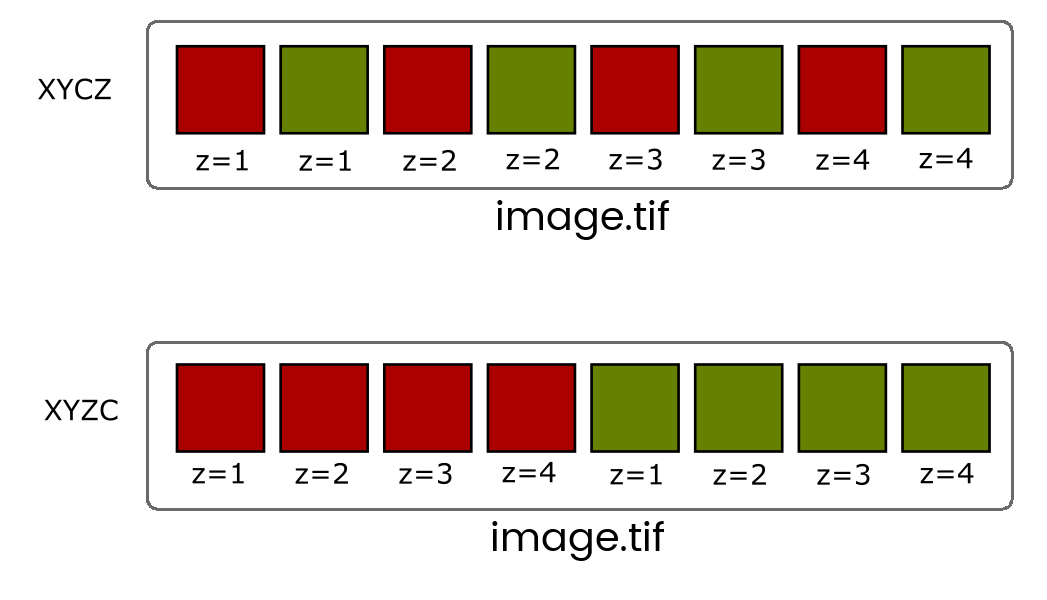
When more than one dimension (time, z, channel) is included, the images are still stored in a linear stack so it's critical to know the dimension order (eg, XYCZT, XYZTC etc) so you can navigate the stack correctly.
You will very rarely have to deal with Interleaved stacks because of Hyperstacks which give you independent control of dimensions with additional control bars.
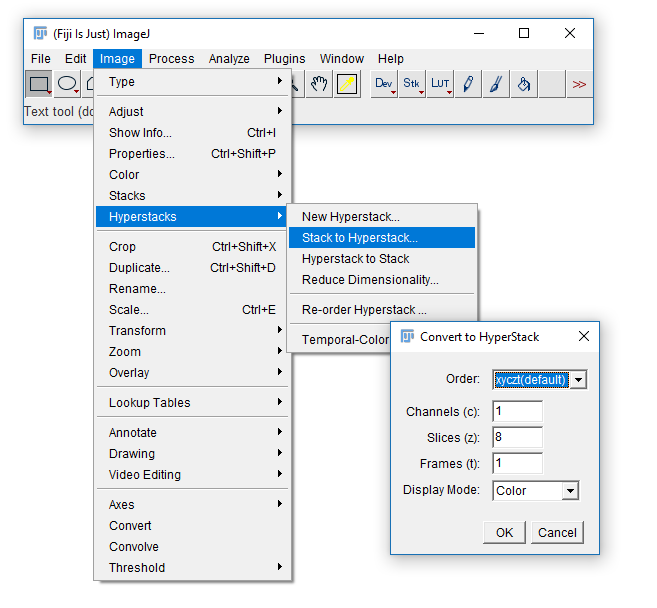
Convert between stack types with the [Image > Hyperstack] menu
Multichannel images are handled as stacks
Interacting with channels is so common that there is a dedicated Channels Tool for additional controls:
[Image > Color > Channels Tool][Image > Type > RGB Color]: convert from 3 channel stack to RGB[Image > Type > RGB Stack]: split RGB image into 3 channel stack
Other useful menu options:
Exercise 4
- Open
Task4.pdfand follow the instructions there. - You will need this image:
06-MultiChannel.tif
Color in Digital Imaging
What is color? How and when to use LUTs
Color in your images is (almost always) dictated by arbitrary lookup tables
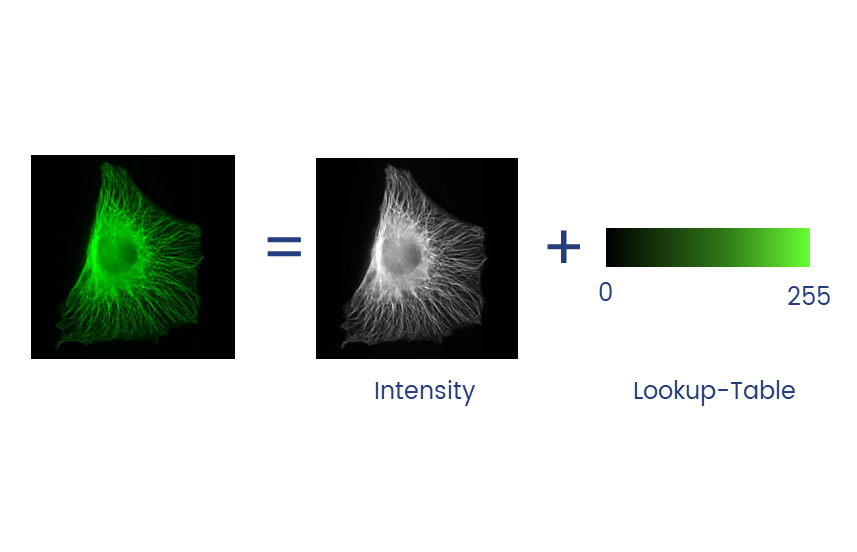
Lookup tables (LUTs) translate an intensity (1-256 for 8 bit) to an RGB display value
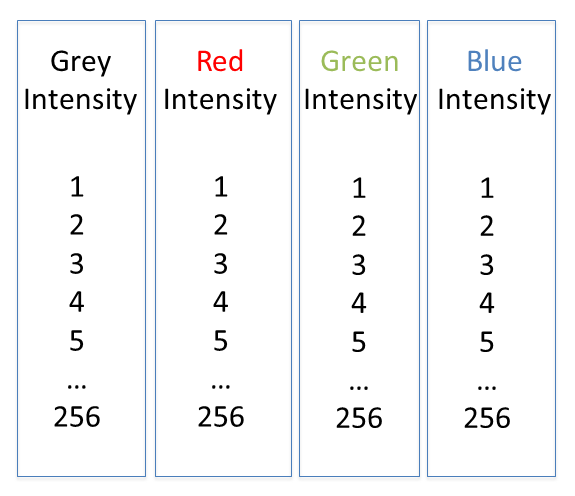
Color in your images is (almost always) dictated by arbitrary lookup tables
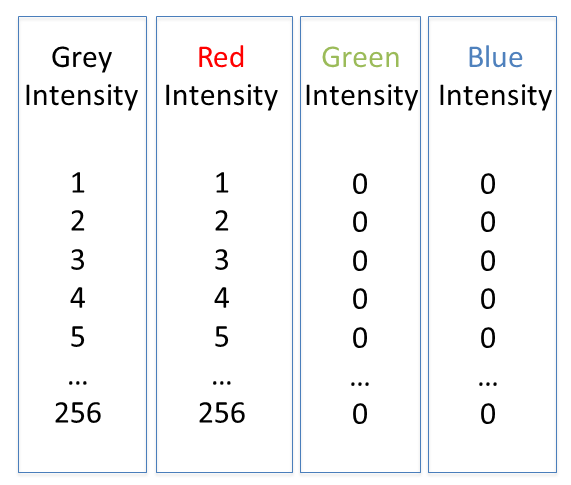
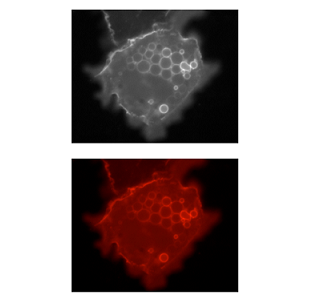
Lookup tables (LUTs), also called "colormaps" translate an intensity (1-256 for 8 bit) to an RGB display value
You can use whatever colours you want (they are arbitrary after all), but the most reliable contrast is greyscale
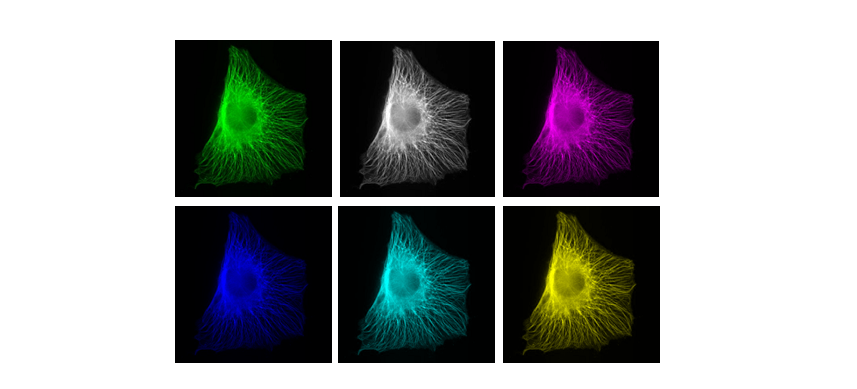
More info on color and sensitivity of the human eye here
Additive and Subtractive Colours can be mixed in defined ways

Non 'pure' colours cannot be combined in reliable ways (as they contain a mix of other channels)
BUT! Interpretation is highly context dependent!
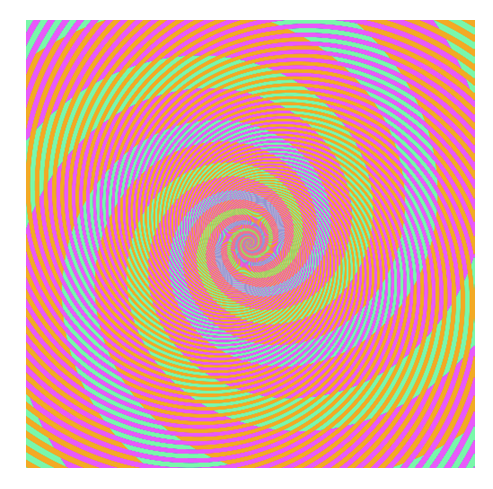
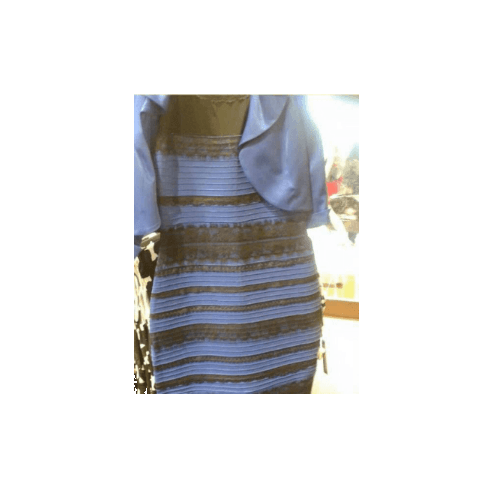




~10% of the population have trouble discerning Red and Green. Consider using Green and Magenta instead which still combine to white.
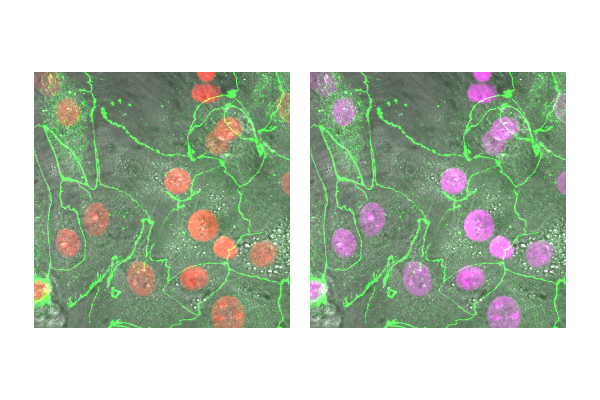
Exercise 5
- Open
Task5.pdfand follow the instructions there. - You will need this image:
06-MultiChannel.tif
A couple of useful LUTs:
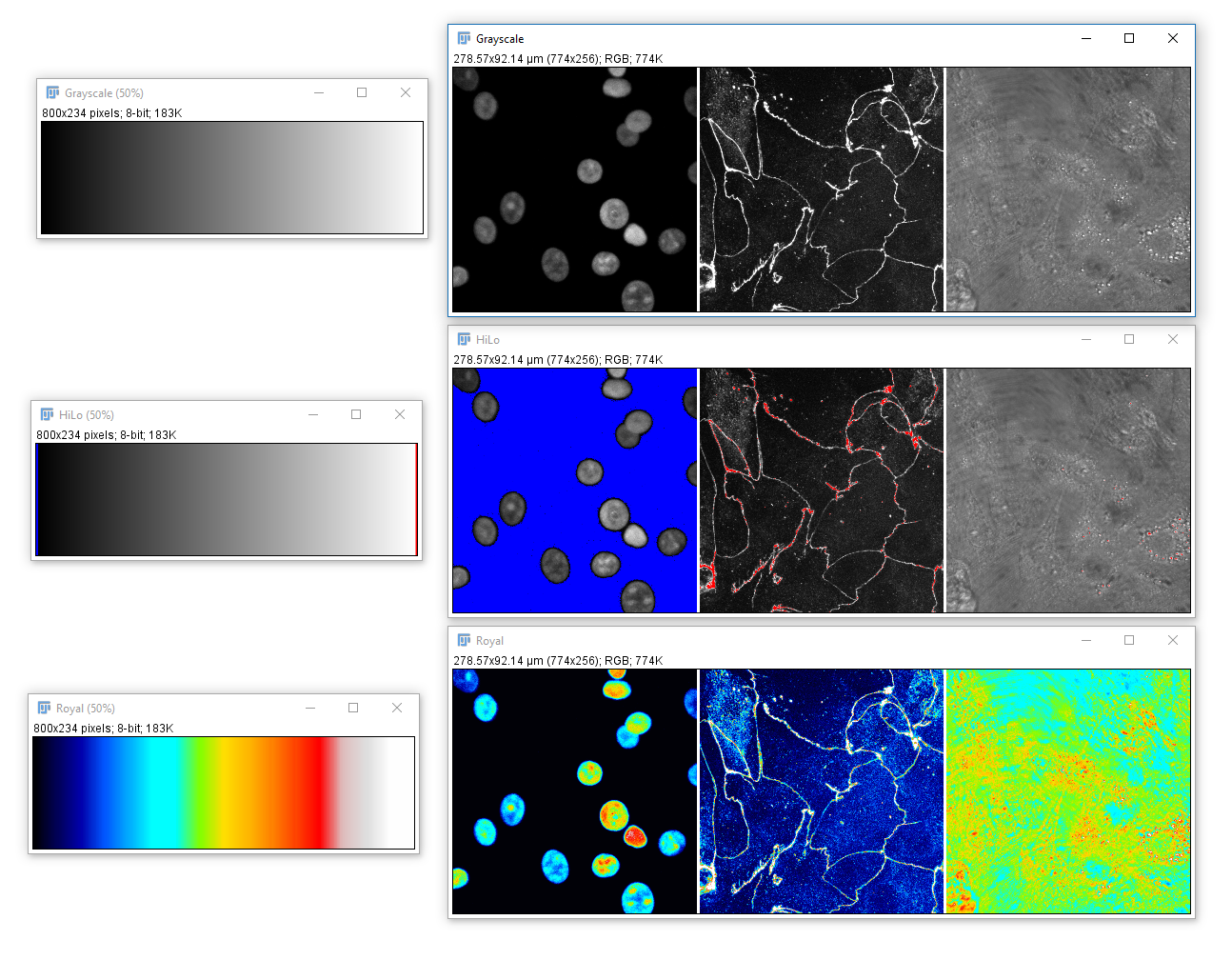
Applications
Applications: Segmentation
What is segmentation? thresholding, Connected Component Analysis
Segmentation is the separation of an image into regions of interest
Semantic segmentation assigns each pixel to a class, e.g. foreground vs. background
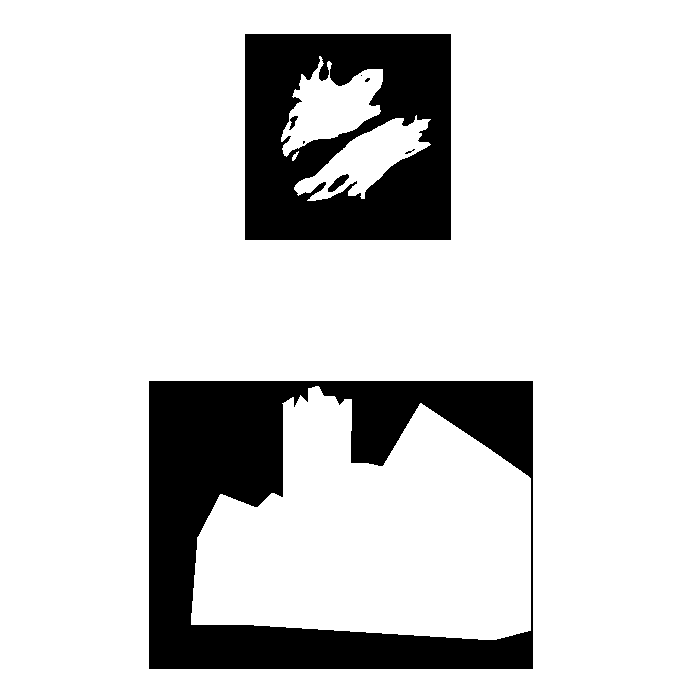
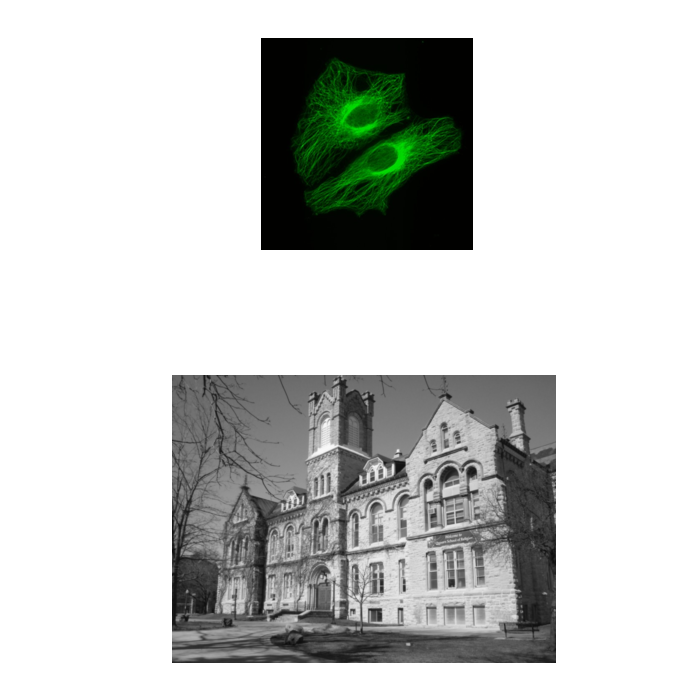

The end point for most segmentation is a binary mask (false/true, 0/255)
Fiji has an odd way of dealing with masks
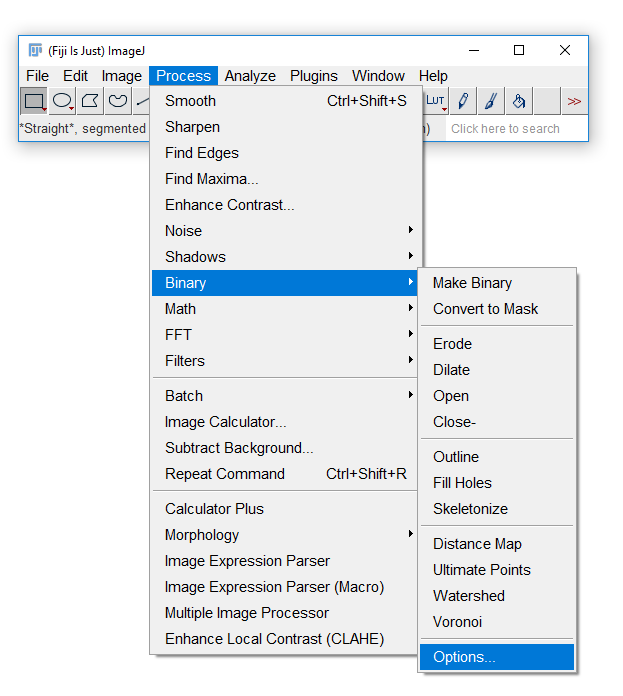
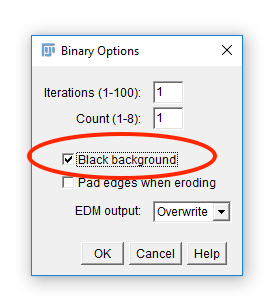
Run [Process > Binary > Options] and check Black Background. Hit OK.
For most applications, intensity-based thresholding works well. This relies on the signal being higher intensity than the background.
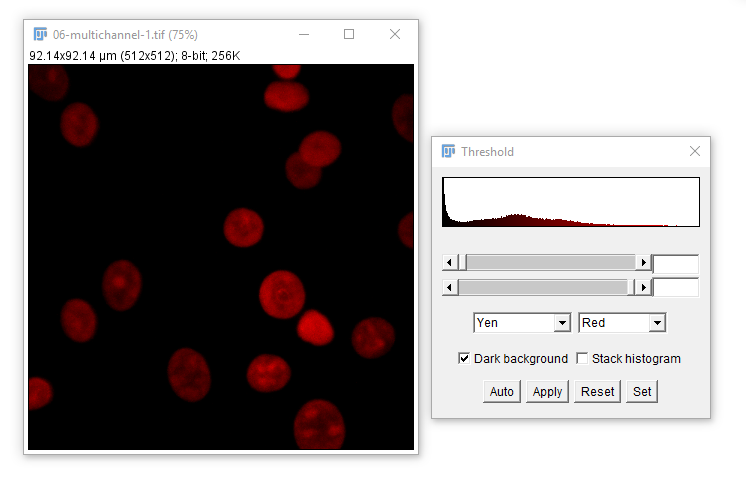
We use a Threshold to pick a cutoff.
A background/foreground binary mask (false/true, 0/255) may be sufficient for some analysis.
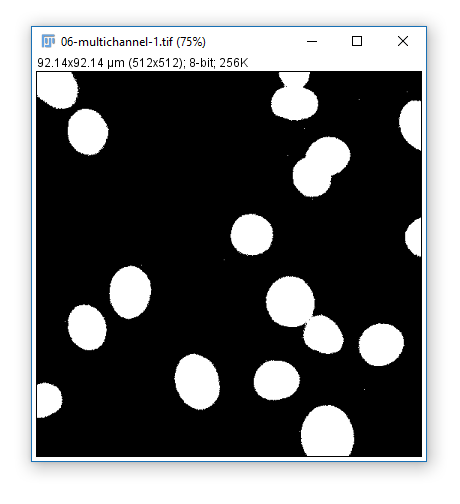
Or we may want to identify individual objects (instance segmentation)
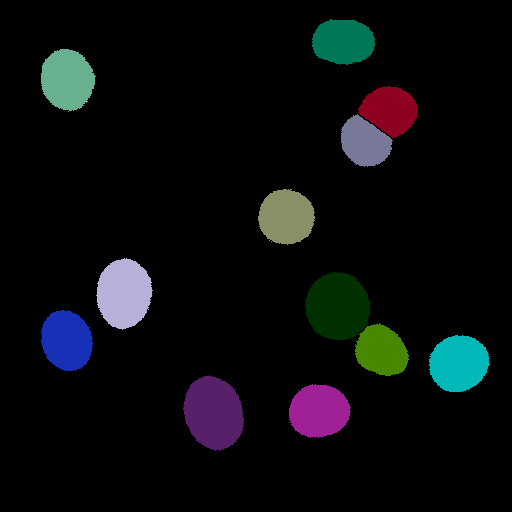

One approach to identifying individual objects when given a binary mask is Connected Component Analysis/Labeling (CCA)
This approach assigns pixels that are touching (connected) to individual object:
4-way connected
- + -
|
8-way connected
+ + + |
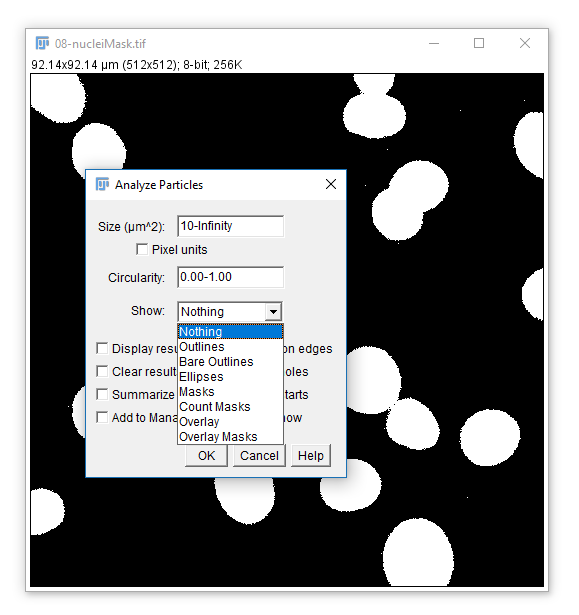
In Fiji this can be accomplished using [Analyze > Analyze Particles...]
If CCA results in merged objects due to touching, then "watershed" approach is frequently used to define boundaries.
Exercise 6
Open Task6.pdf and follow the instructions there.
You will need these images: 07-nuclei.tif and 08-nucleiMask.tif
Analyze Particles comes with the option to Display Results
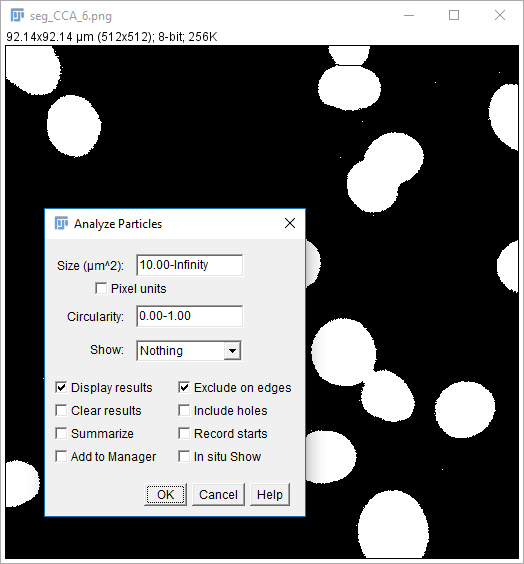
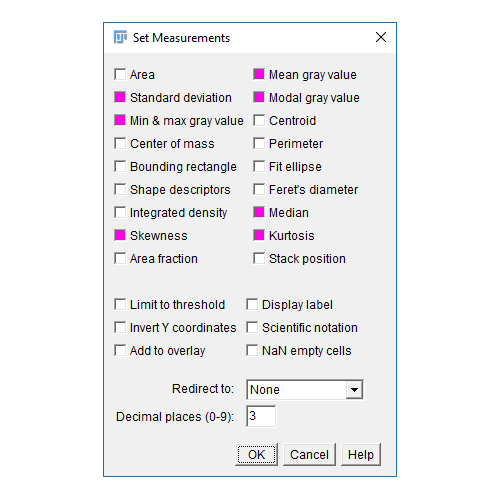
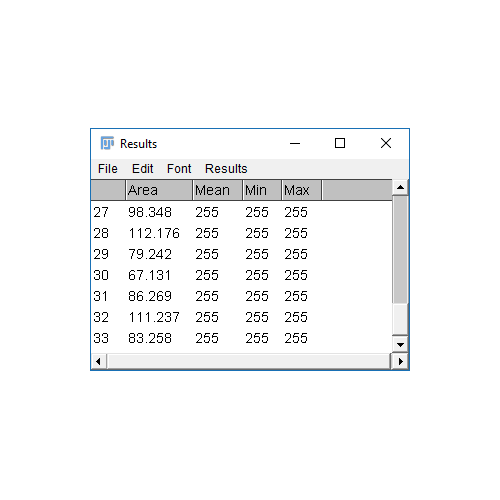
- The results table will have a column for anything selected in
[Analyze > Set Measurements]and one row per object - Measurements (including intensity - labelled purple above) are made on the mask!
To apply measurements to the original image: check Add to Manager in Analyze Particles, open the original image, then run [More > Multi Measure]
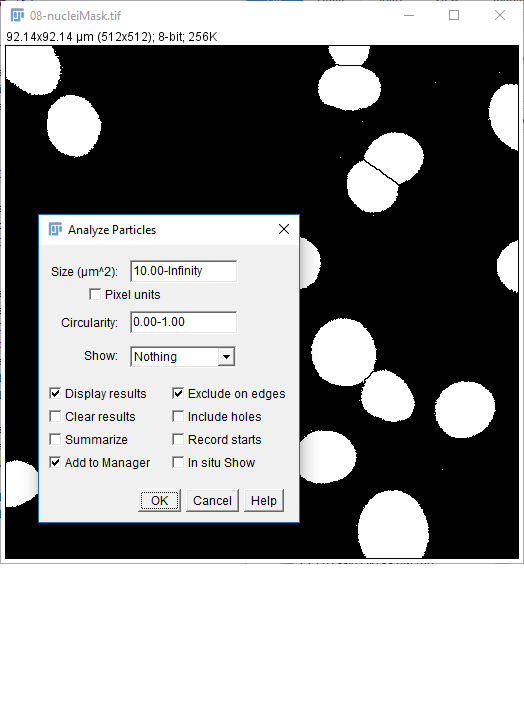
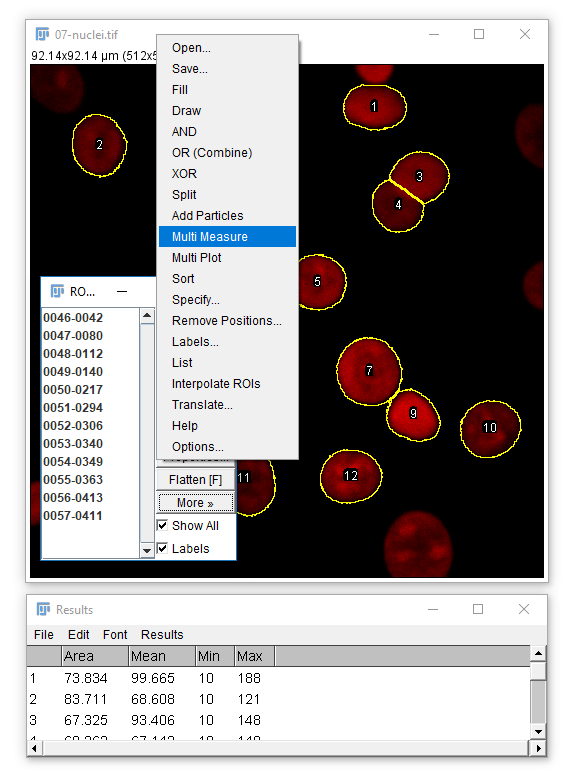
Don't forget [Analyze > Set Measurements] to pick parameters
You may want to create an output or display image showing the results of CCA or segmentation. Analyze particles has several useful outputs:
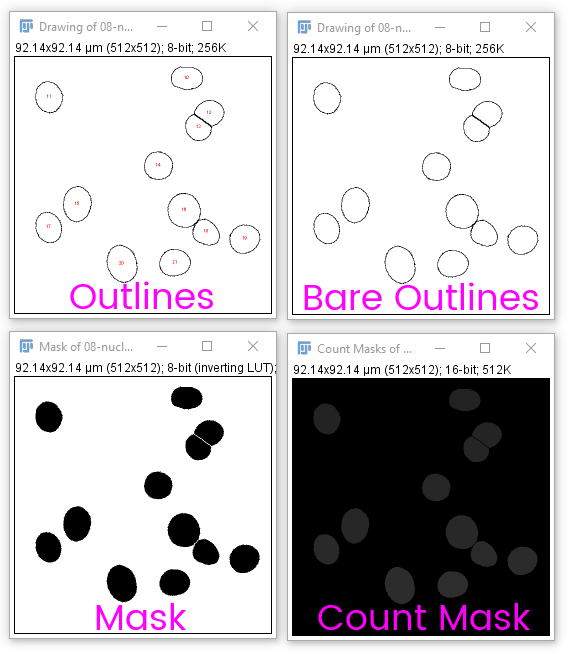
Count masks are very useful in combination with [Image > Look Up Tables > Glasbey]-style (IE random) LUTs
Applications: Colocalisation
Use cases, some simple guidance, JaCoP
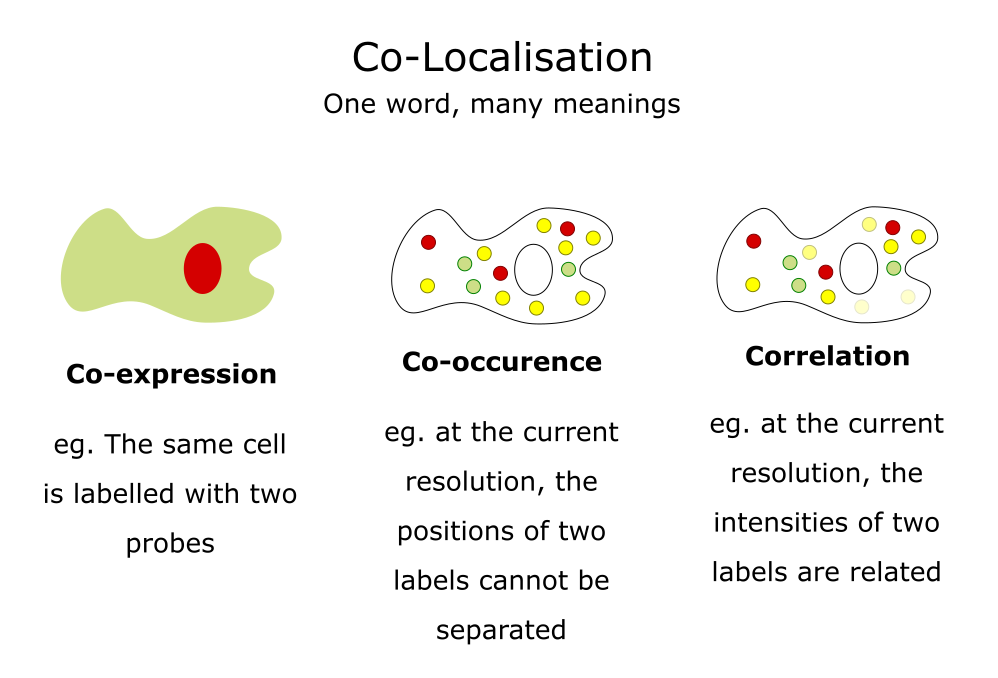
Adapted from a slide by Fabrice Cordelieres
For more rigor, see: Aaron et al. J Cell Sci (2018) 131 (3): jcs211847., Figure 4
Colocalisation is highly dependent upon resolution! Example:
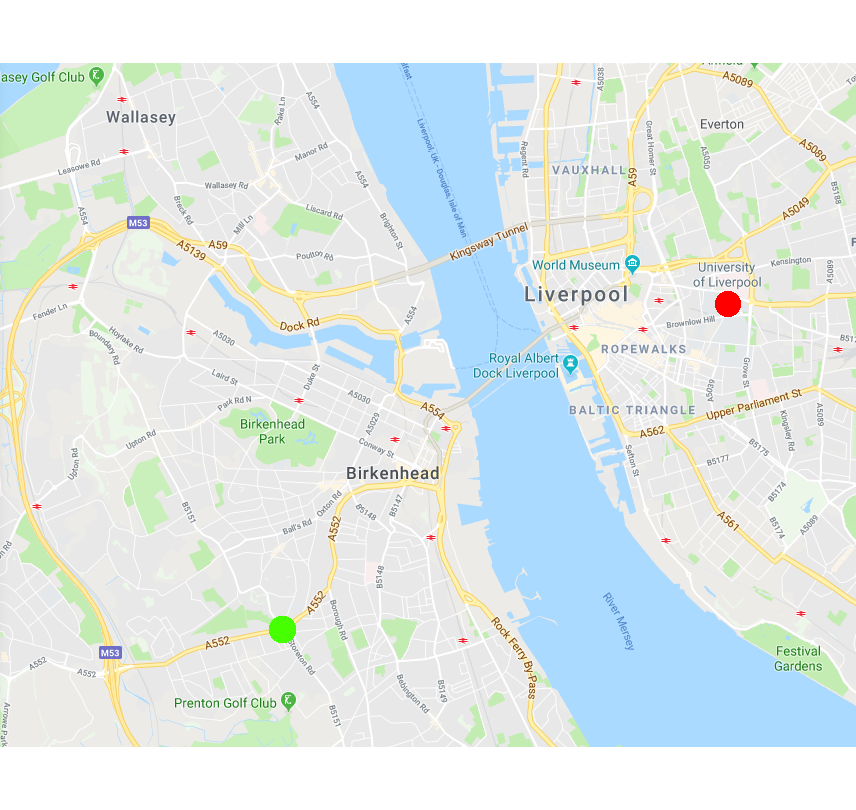
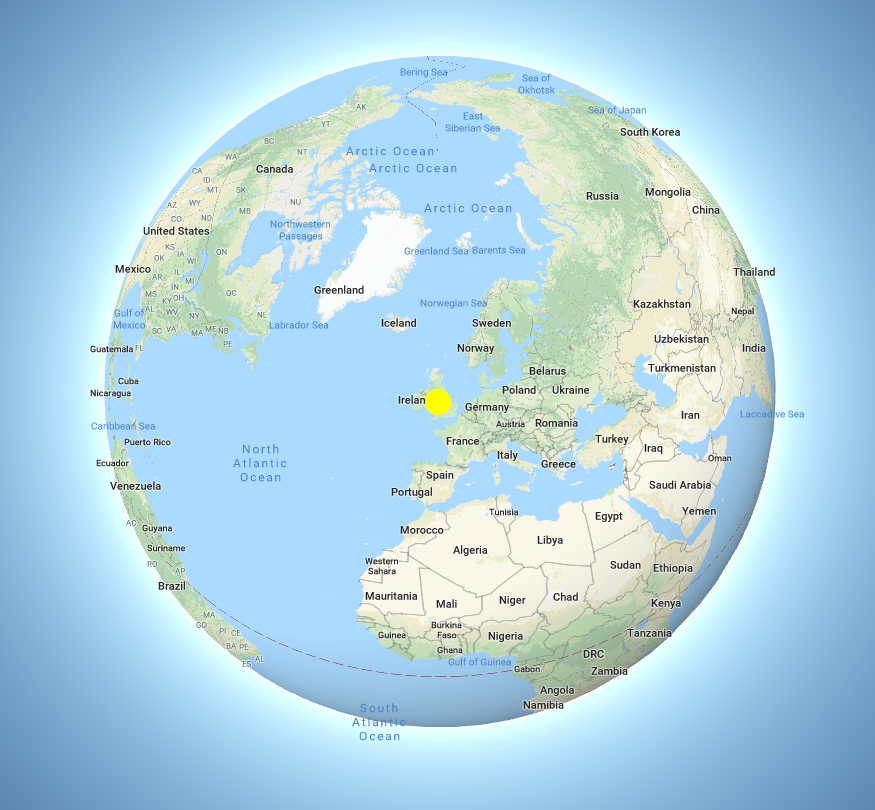
Same idea goes for cells. Keep in mind your imaging resolution!
We will walk through using JaCoP (Just Another CoLocalisation Plugin) to look at Pearson's and Manders' analysis
It's been revamped by the BIOP folks of EPFL: JaCoP-BIOP
The companion paper https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2818.2006.01706.x

Pearson's Correlation Coefficient
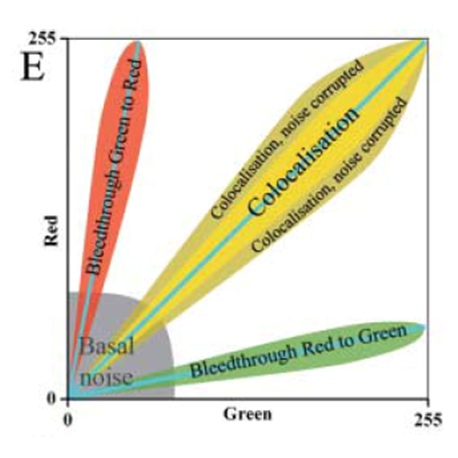
- For each pixel, plot the intensities of two channels in a scatter plot
- Ignore pixels with only one channel (IE intensity below BG)
- P value describes the goodness of fit (-1 to 1)
- 1 = perfect correlation
- 0 = no positive or negative correlation
- -1 = exclusion
Figure from https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2818.2006.01706.x
Exercise: PCC
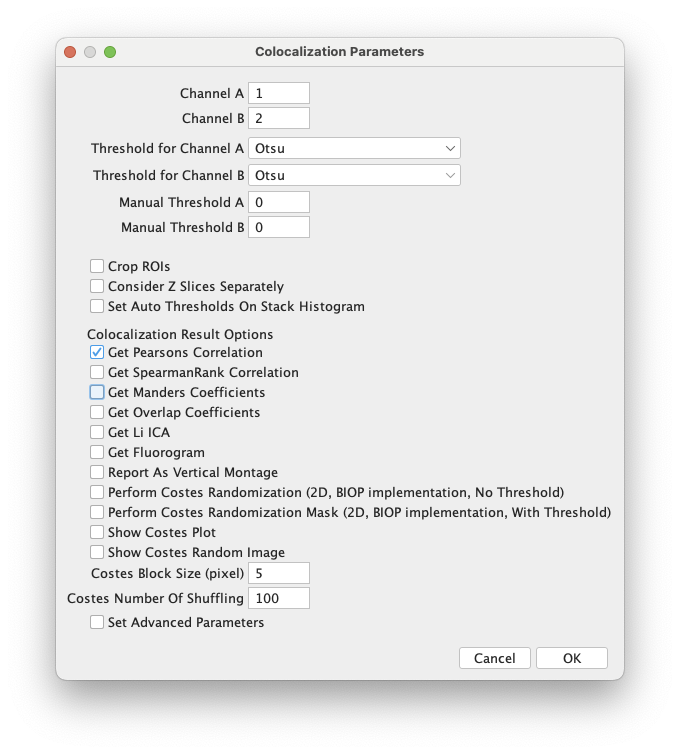
- Download
JaCoP-BIOP plugin - Run
[Plugins > Install...], point to the downloaded jar file, then press "Save" to confirm - Restart Fiji
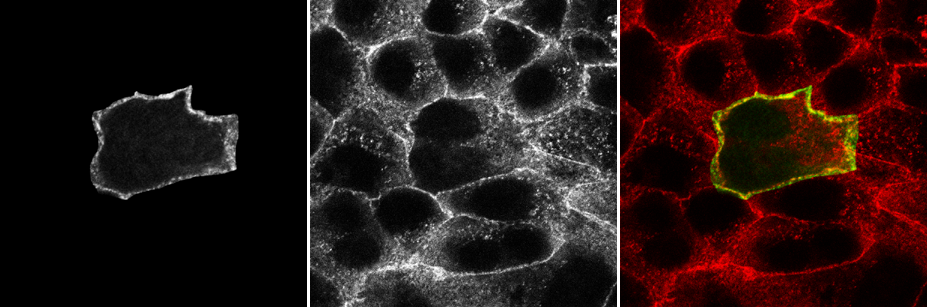
- Open
11-coloc-multichannel.tif.
This is a multichannel version of the images to the left; use the[Image > Color > Channels tool]command to examine the channels - Run
[Plugins > BIOP > Image Analysis > BIOP JaCoP] - Uncheck everything except `Get Pearsons Correlation`.
- At the top, select different channels, by number, for `Channel A` and `Channel B`
- Repeat for different combinations of pairs of channels.

- Great for complete colocalisation
- Unsuitable if there is a lot of noise or partial colocalisation (see below)
- Midrange P-values (-0.5 to 0.5) do not allow reliable conclusions to be drawn
- Bleedthrough can be particularly problematic (as they will always correlate)
Manders' Overlap Coefficient
- Removes some of the intensity dependence of Pearson's and provides channel-specific overlap coefficients (M1 & M2)
- Values from 0 (no overlap) to 1 (complete overlap)
- Defined as "the ratio of the summed intensities of pixels from one channel for which the intensity in the second channel is above zero to the total intensity in the first channel"
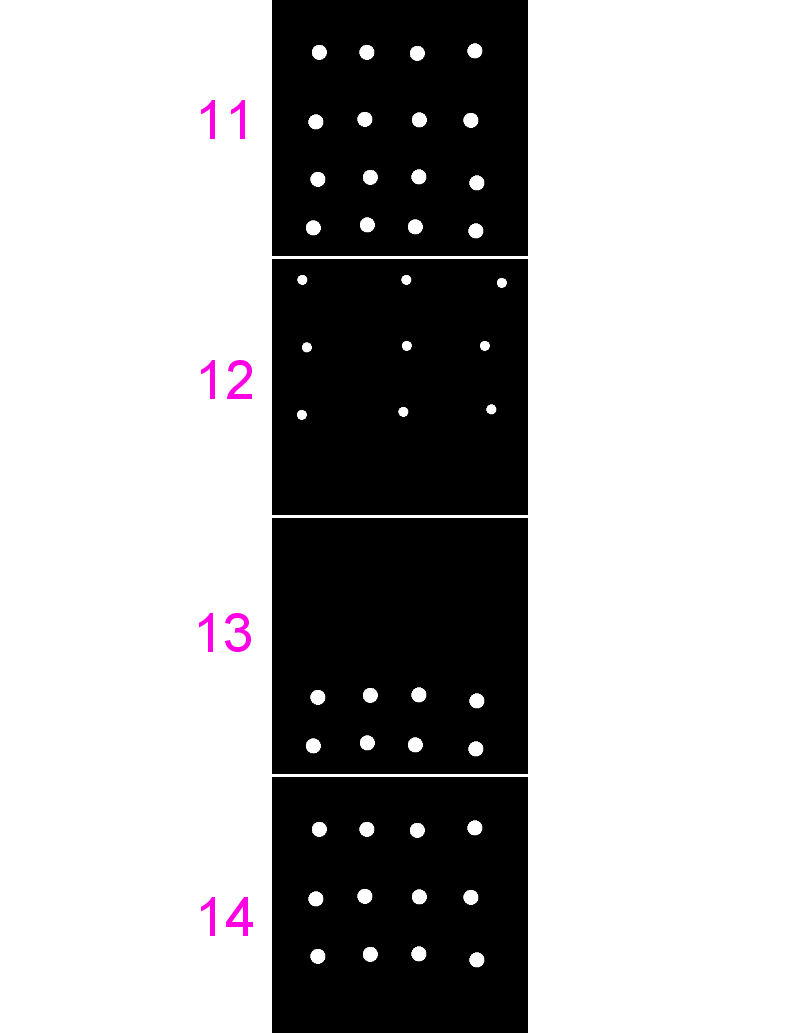
Exercise: Manders'

- Use the same multichannel image from last time (
11-coloc-multichannel.tif) - Run
[Plugins > BIOP > Image Analysis > BIOP JaCoP], check both `Get Pearsons Correlation` and `Get Manders coefficients` - Run for different combinations of these images
- Note the differences in coefficients especially in images 13 and 14
- [BONUS] add some noise
[Process > Noise > Add Noise]or blur your images[Process > Filters > Gaussian Blur]and see how that affects the coefficients
Applications: Tracking
Correlating spatial and temporal phenomena, Feature detection, linkage, gotchas
Life exists in the fourth dimension. Tracking allows you to correlate spatial and temporal properties.
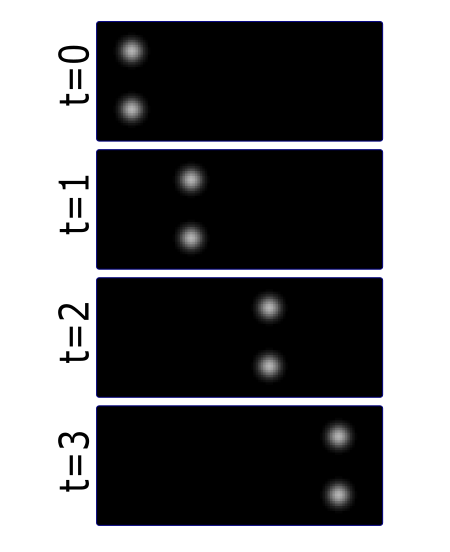
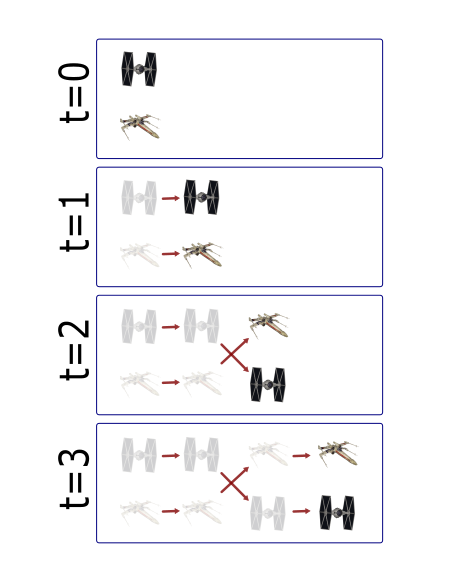
Most partcles look the same! Without any way to identify them, tracking is probabilistic.
Tracking has two parts: Feature Identification and Feature Linking
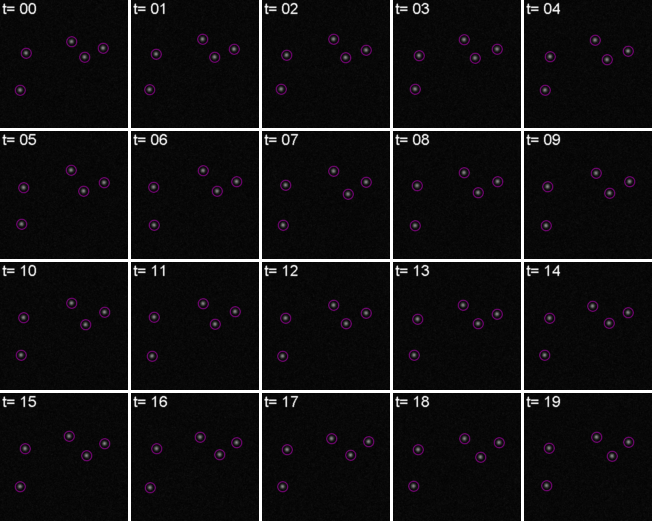
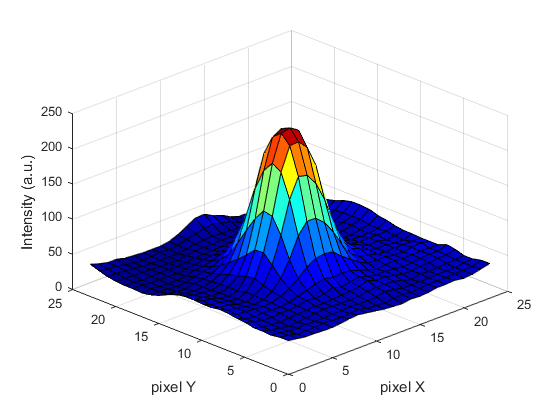
For every frame, features are detected, typically using a Gaussian-based method (eg. Laplacian of Gaussian: LoG)
Spots can be localised to sub-pixel resolution!
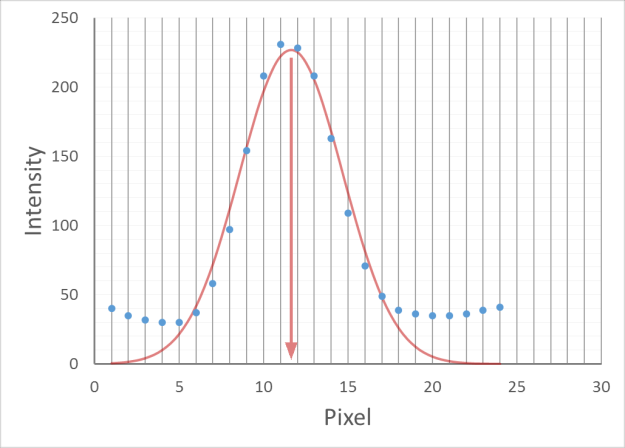
Without sub-pixel localisation, the precision of detection is limited to whole pixel values.
Feature linkage
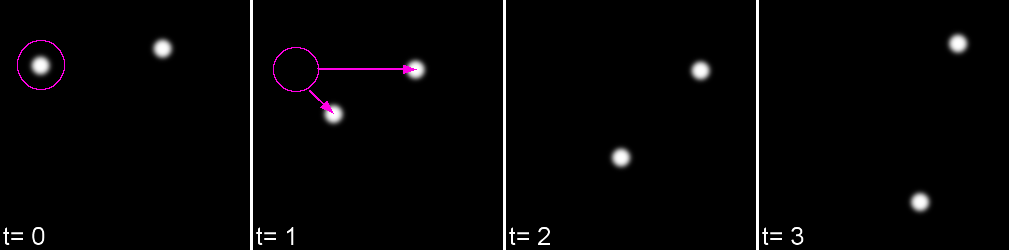
For each feature, all possible links in the next frame are calculated. This includes the spot disappearing completely.
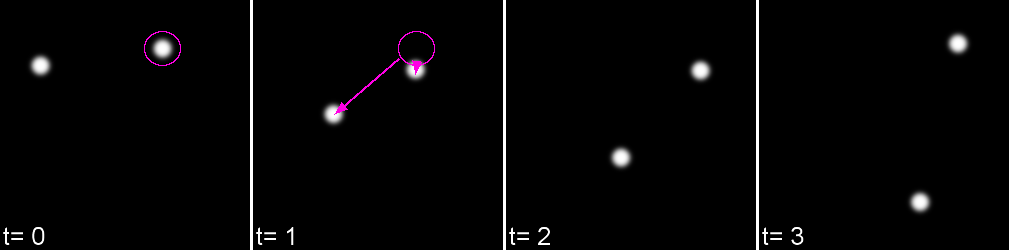
A 'cost matrix' is formed to compare the 'cost' of each linkage. This is globally optimised to calculate the lowest cost for all linkages.
In the simplest form, a cost matrix will usually consider distance. Many other parameters can be used such as:
- Intensity
- Shape
- Quality of fit
- Speed
- Motion type
Which can allow for a more accurate linkage especially in crowded or low S/N environments
Exercise: Tracking
Open 10-tracks.tif
Hit the arrow to play the movie. Right Click on the arrow to set playback speed
If you're interested in how the dataset was made see this snippet
Run [Plugins > Tracking > Trackmate]
If it's missing, download the TrackMate plugin and install it using [Plugins > Install...]
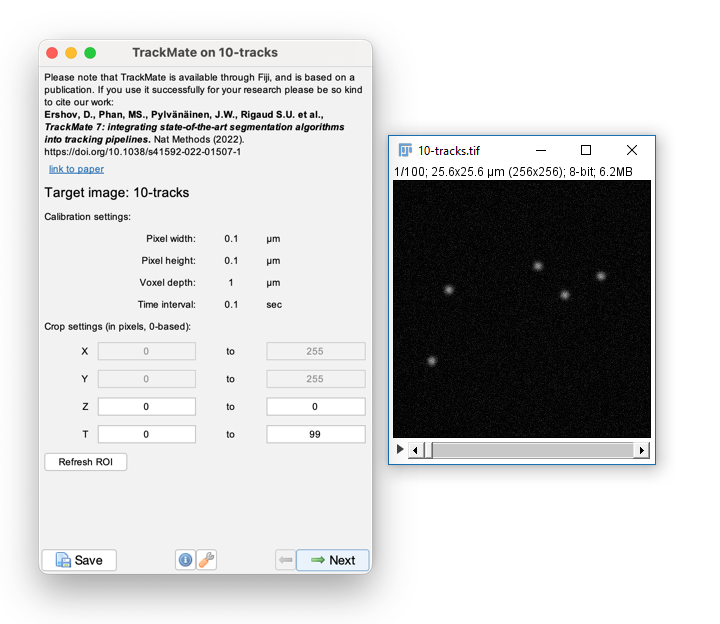
- Trackmate guides you through tracking using the Next and Prev buttons
- The first dialog lets you select a subset (in space and time) to process. This is handy on large datasets when you want to calculate parameters before processing the whole dataset
- Hit Next, keep the default (LoG) detector then hit Next, and advance the slides!
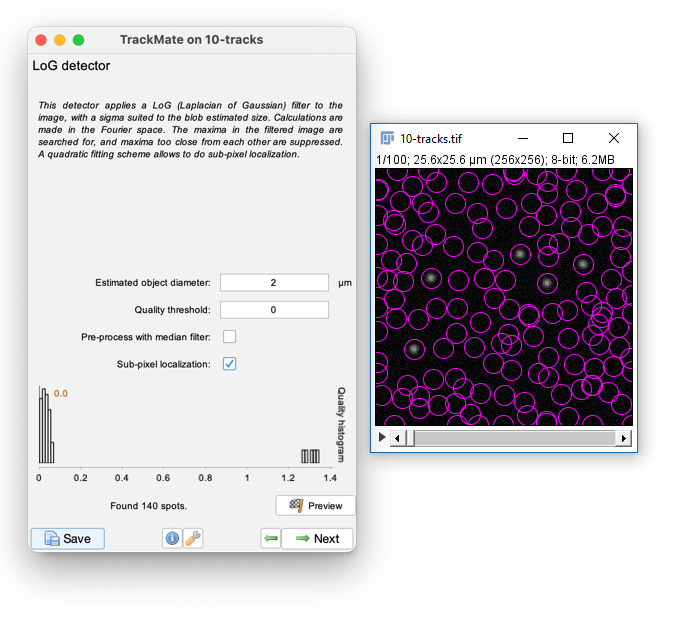
- Enter a Blob Diameter of 2 (note the scaled units)
- Hit preview. Without any threshold, all the background noise is detected as features
- Enter `0.1` for the `Quality threshold` and hit Preview again.
You should aim to set the minimum threshold that removes all noise.
Slide the navigation bar, then hit Preview to check out a few other timepoints. When satisfied press Next and advance the slides!
TrackMate will process the stacks.
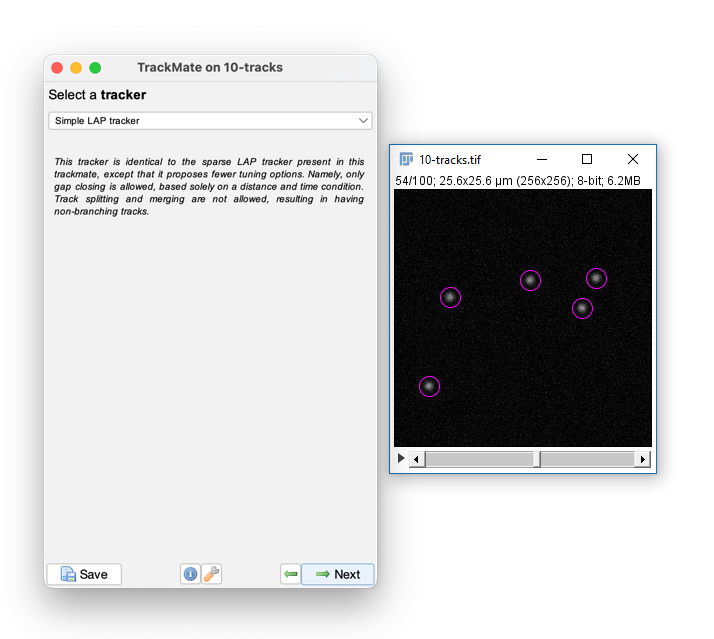
Once it's done, hit next, accepting defaults until you reach 'Select a tracker'
Ensure `Simple LAP tracker` is selected and hit Next, then advance the slides!
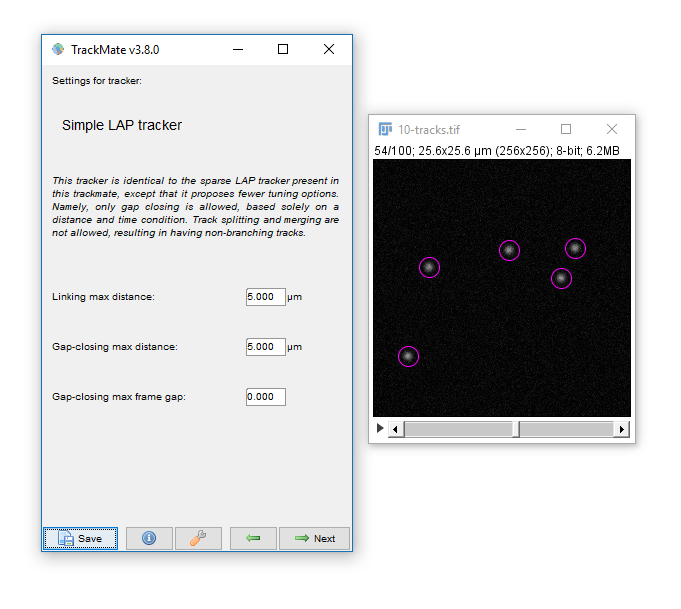
In the 'Settings for Simple LAP tracker', set:
- `Linking max distance` to `5.0`
- `Gap-closing max distance` to `5.0`
- `Gap-closing max frame gap` to `0`
Press Next and after processing, you should have tracks!

Linking Max Distance Sets a 'search radius' for linkage
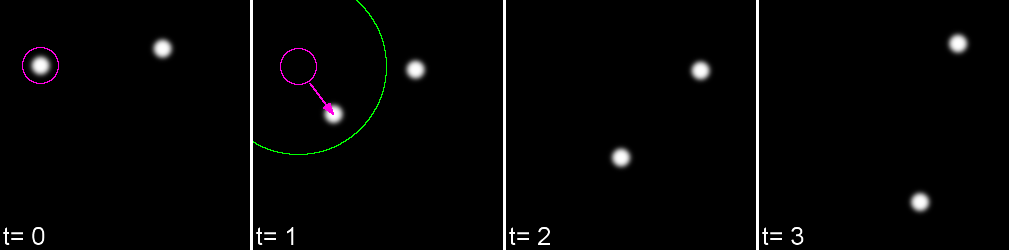
Gap-closing Max Frame Gap Allows linkages to be found in non-adjacent frames
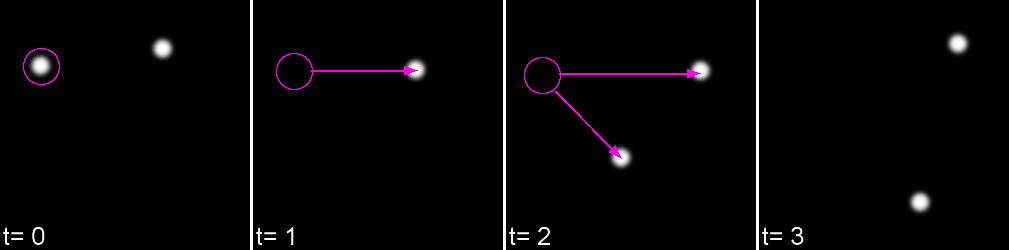
Gap-closing Max Distance Limits search radius in non-adjacent frames
Press Next to get to outputs from Trackmate: (1) Tracking data
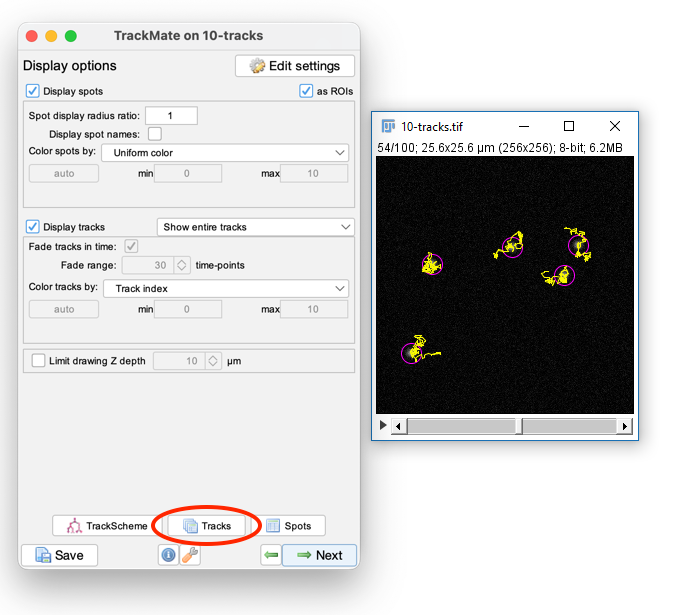
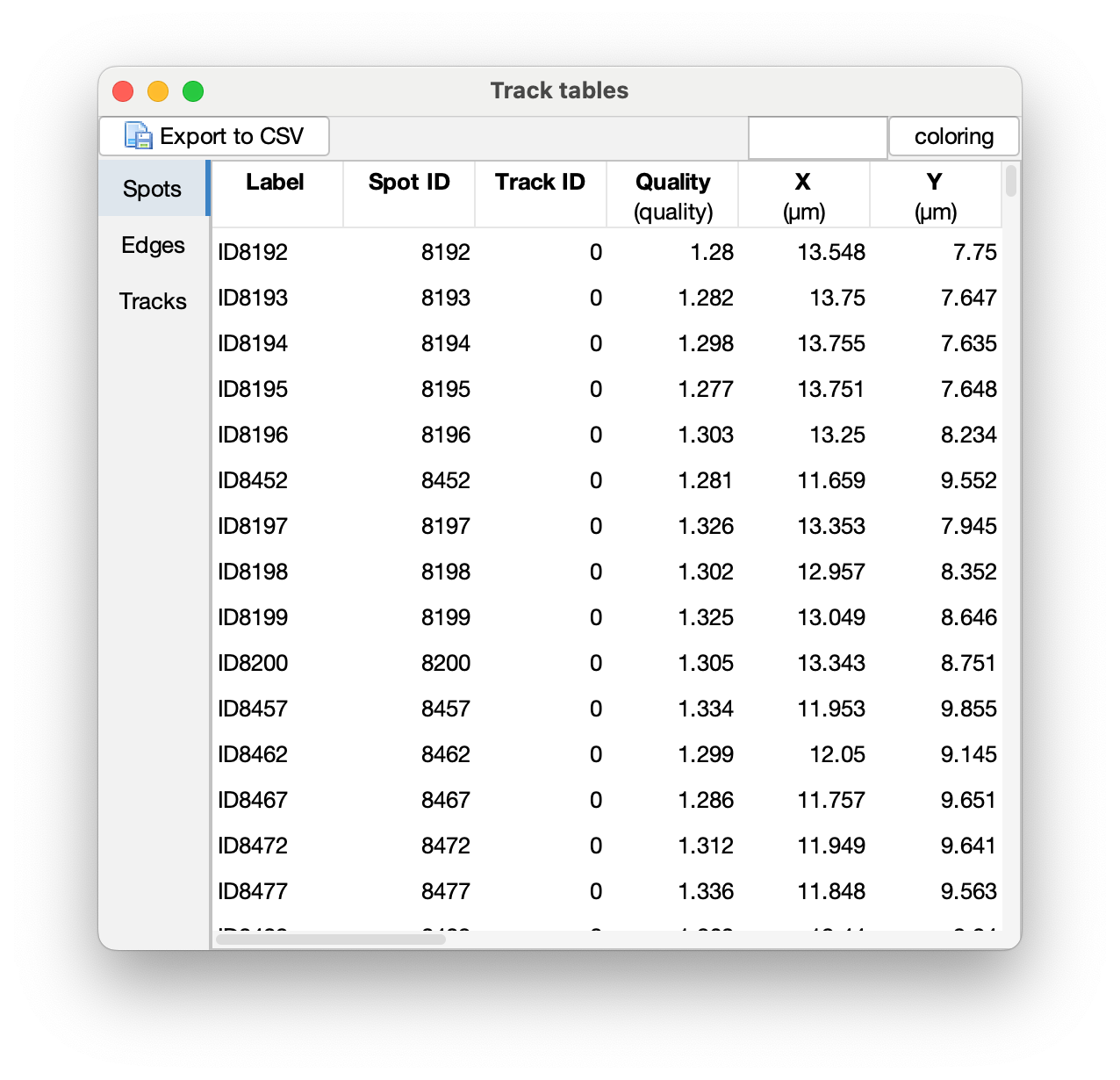
Press Next to get to outputs from Trackmate: (2) Movies!
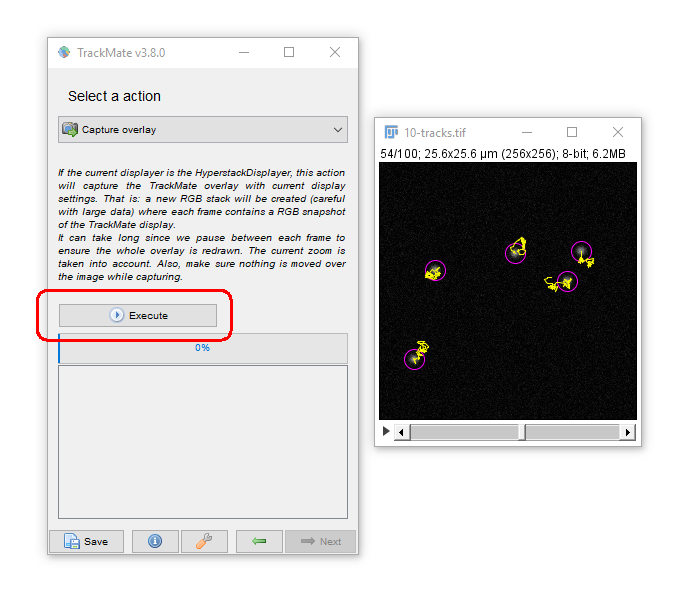

You may want adjust the Display Options to get the tracks drawing the way you want (e.g. try "Local, Backwards")
While simple, Tracking is not to be taken on lightly!
- For the best results make sure the inter-particle distance is greater than the frame-to-frame movement. If not, try to increase resolution (more pixels) or decrease interval (more frames)
- The search radius increases processing time with HUGE datasets but in most case, has little effect on processing time. Remember that closer particles will still be linked preferably if possible.
- Keep it simple! Unless you have problems with noise, blinking, focal shifts and similar, do not introduce gap closing as this may lead to false-linkages
- 'Simple LAP tracker' does not include merge/spliting events, however Trackmate ships with the more complex 'LAP Tracker' which can handle merge/splitting events (but keep in mind your system!)
- Quality control! Look at your output carefully and make sure you're not getting 'jumps' where one particle is linked to another incorrectly
Applications: Stitching
Resolution vs field size, stitching, using overlaps, issues and bugs
Increasing resolution (via higher NA lenses) almost always leads to a reduced field

Often you will want both!
We can achieve this with tile scanning (IE. imaging multiple adjacent fields)
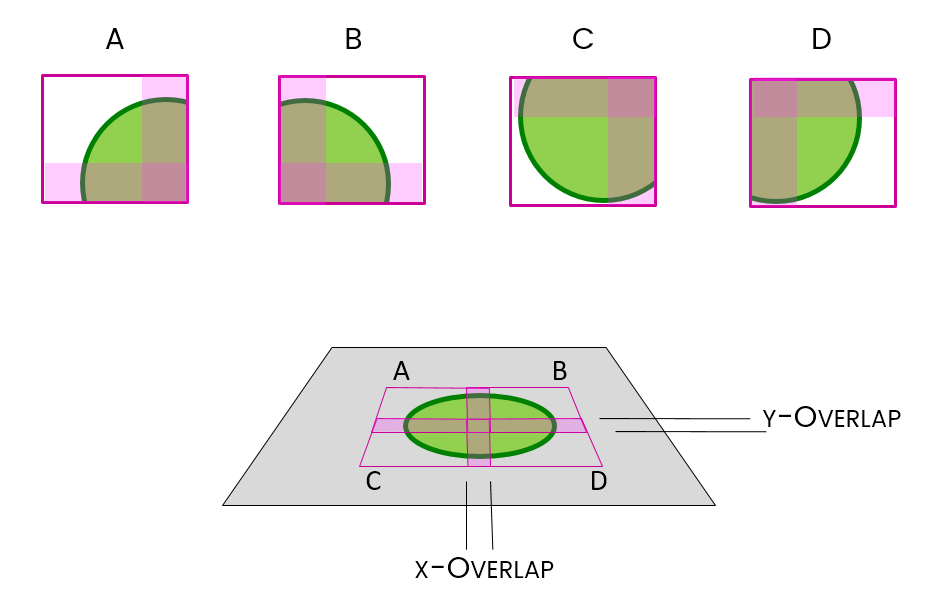
Stitching is the method used to put them back together again.
We'll use the Grid/Collection Stitching plugin
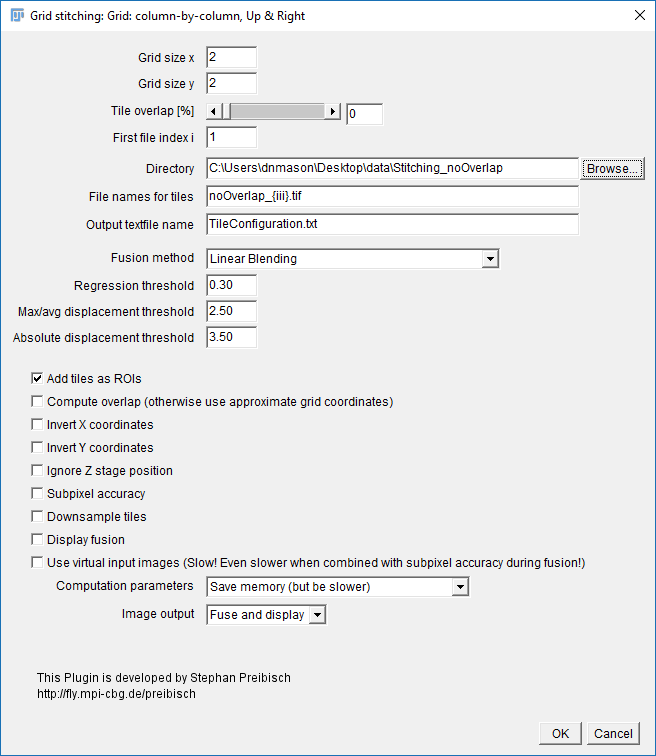
Exercise: No-overlap Stitching
- Download and unzip
Stitching_noOverlap.zip(make a note of the location) - Run
[Plugins > Stitching > Grid/Collection Stitching] - Select: Column by Column | Up & Right , then press OK.
- Settings:
- Grid Size: 2x2
- Tile Overlap: 0
- Directory: {path to your folder}
- File Names for tiles: noOverlap_{iii}.tif
- Uncheck all the options [OPTIONAL] Check `Add tiles as ROI`
- Hit OK (accept fast fusion)
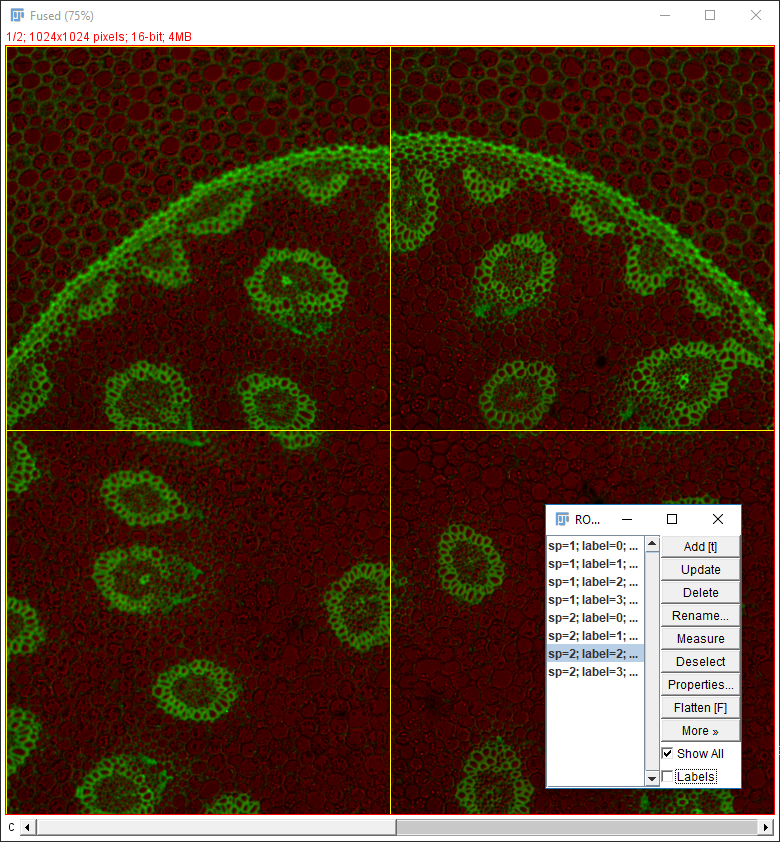
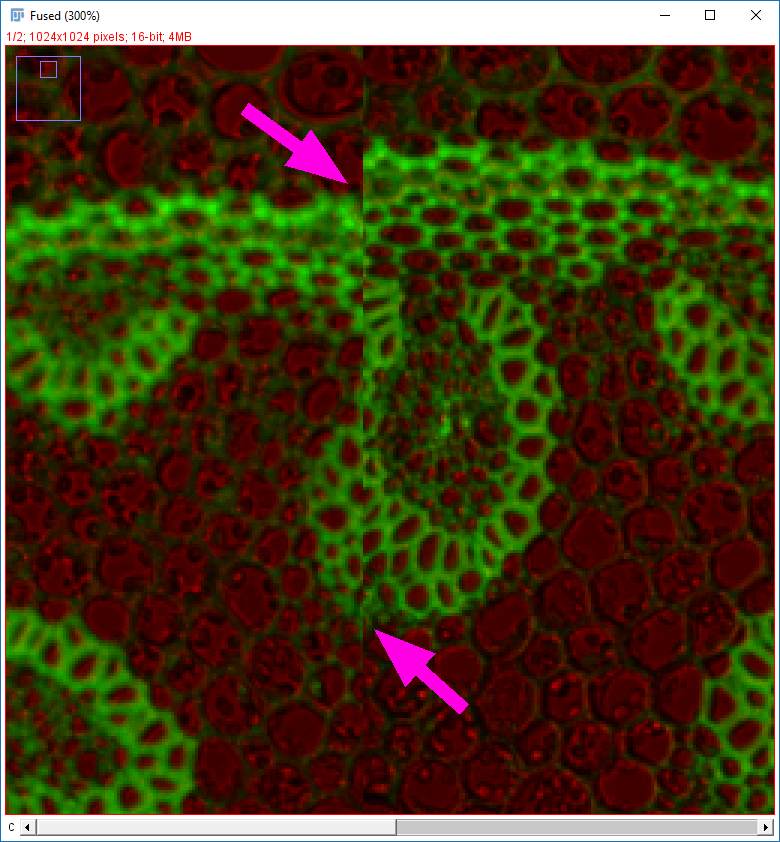
Why do the images not line up?
Exercise: Stitching with Overlap
- Open
Stitching_Overlap.zip. Unzip to the desktop. - Run
[Plugins > Stitching > Grid/Collection Stitching]again - Use the same Grid settings (they should have been restored).
- Set `Tile overlap` to `10%`
- Update the Directory to the new path "Stitching_Overlap"
- File Names for tiles: overlap_{iii}.tif
- Ensure `Compute overlap` is checkeds
- Hit OK
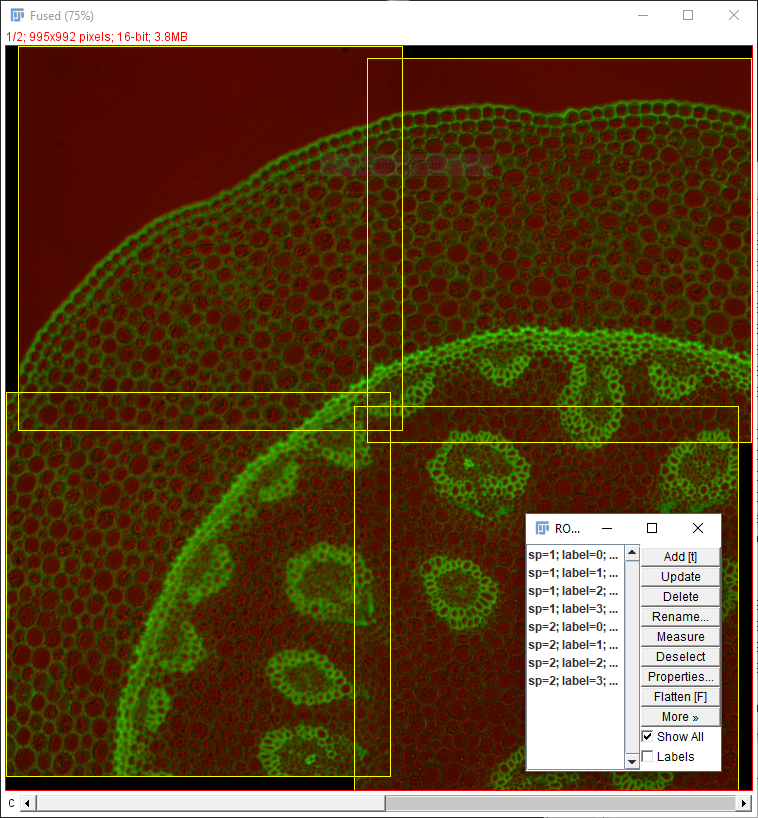
Two things to remember when using Grid/Collection Stitching:
- Default (R,G,B) LUTs are used after stitching
- All calibration information is stripped
- Stitching will have a harder time with sparse features or uneven illumination (example in epilogue)
The most important point is to know your data!
- Grid layout (dimensions and order!)
- Overlap
- Calibration
Applications: Batch Processing
Why batch process? File conversion, batch processing, scripting
Manual analysis (while sometimes necessary) can be laborious, error prone and not provide the provenance required. Batch processing allows the same processing to be run on multiple images.
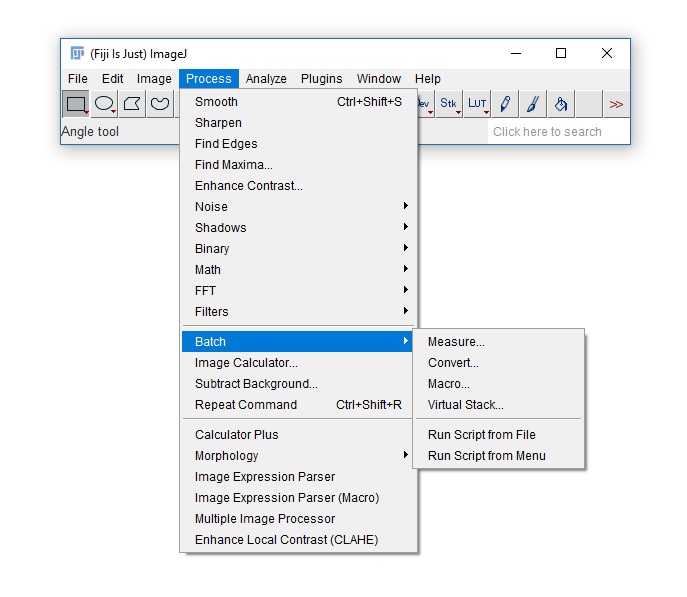
The built-in [Process > Batch] menu has lots of useful functions:
We'll use a subset of dataset BBBC008 from the Broad Bioimage Benchmark Collection
- Download the zip file from here to the desktop
- Unzip (right click and "Extract All") to end up with a folder on your desktop called
BBBC008_partial
- Make another folder on the desktop called
Output
Exercise 7: Batch Convert
- Ensure you have the the zip file
BBBC008_partial.zipextracted to a known location and a that you have a second folder called "Output" next to it. - Open
Task7.pdfand follow the instructions there.
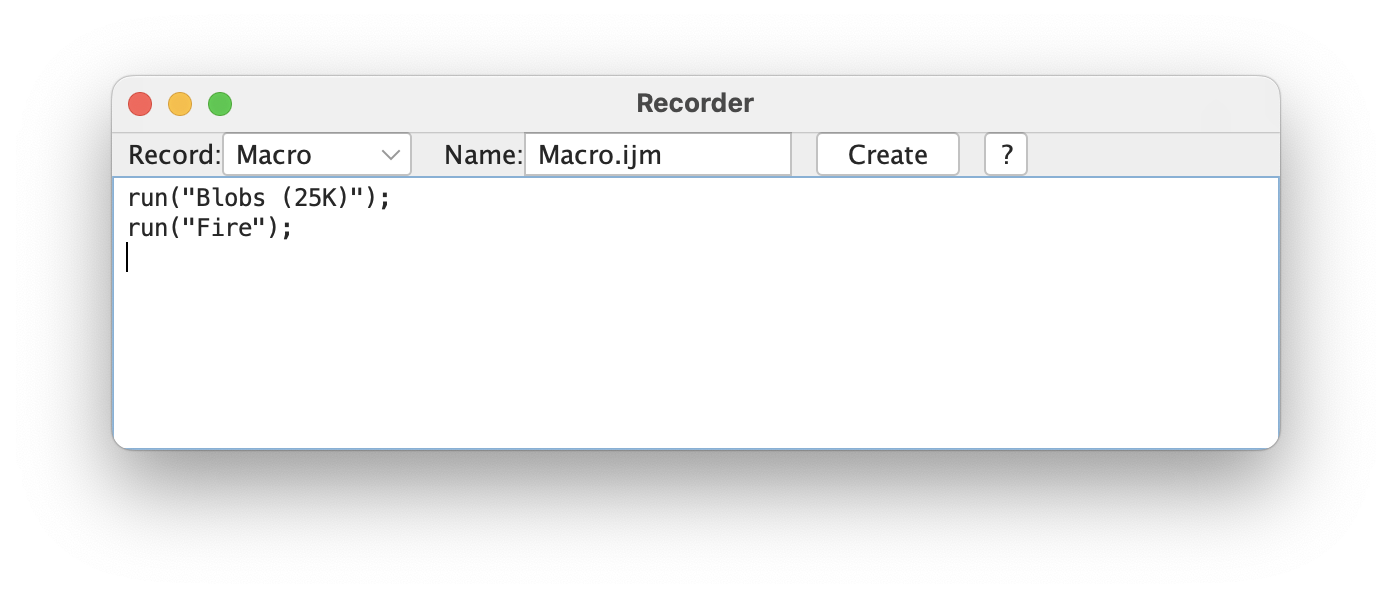
[Plugins > Macros > Record...]can enable you to generate simple macros without having to write them yourself.
- With the Recorder open, (almost) every action you take in Fiji will be recorded as a macro command--this includes many Plugin functions!
- The recorded Macros can be saved ("Create" button and Save) and then re-run
[Plugins > Macros > Run...]
Exercise 8: Macro Recorder
- Ensure you have the the zip file
BBBC008_partial.zipextracted to a known location and a that you have a second folder called "Output" next to it. - Open
Task8.pdfand follow the instructions there.
Scripting
A very brief foray into scripts
Scripting is useful for running the same process multiple times or having a record of how images were processed to get a particular output
Fiji supports many scripting languages including Java, Python, Scala, Ruby, Clojure and Groovy through the script editor which also recognises the macro language from the previous example (which we'll be using)
As an example, we're going to (manually) create a montage from a three channel image, then see what the script looks like
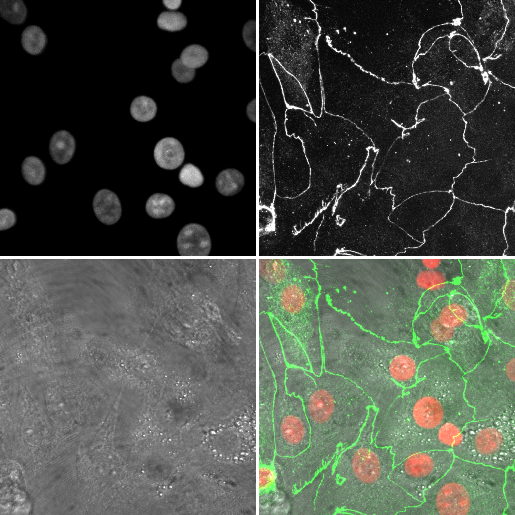
- Open
06-MultiChannel.tif - Open the macro recorder:
[Plugins > Macros > Record]
- (If necessary
[Image > Hyperstacks > Stack to Hyperstack]) - Open the channels tool
[Image > Color > Channels Tool]and set the mode tograyscale - Run
[Image > Type > RGB color] - Rename this image to
channelswith[Image > Rename] - Select the original stack, and using the channels tool, set the mode to
composite - Run
[Image > Type > RGB color] - Rename this image to
mergewith[Image > Rename] - Close the original (it should be the only 8-bit image open (check the Info bar!)
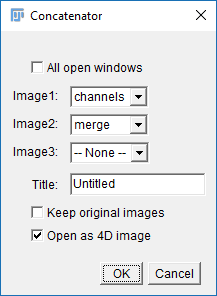
- Run
[Image > Stacks > Tools > Concatenate]and select Channels and merge in the two boxes (see right) - Run
[Image > Stacks > Make Montage]change the border width to 3 then hit OK
Got it? Have a look at the Macro Recorder and see if you can see the commands you ran
Open the script editor with [File > New > Script] and copy in the following code:
//-- Record the filename
imageName=getTitle();
print("Processing: "+imageName);
//-- Display the stack in greyscale, create an RGB version, rename
Property.set("CompositeProjection", "null");
Stack.setDisplayMode("grayscale");
run("RGB Color");
rename("channels");
//-- Select the original image
selectWindow(imageName);
//-- Display the stack in composite, create an RGB version, rename
Property.set("CompositeProjection", "Sum");
Stack.setDisplayMode("composite");
run("RGB Color");
rename("merge");
//-- Close the original
close(imageName);
//-- Put the two RGB images together
run("Concatenate...", " title=newStack open image1=channels image2=merge");
//-- Create a montage
run("Make Montage...", "columns=4 rows=1 scale=0.50 border=3");
//-- Close the stack (from concatenation)
close("newStack");
Open 06-MultiChannel.tif again and hit Run
Comments, variables, print, active window
This script operates on an open image but it's easily converted to a batch processing script using the built in templates:
The full script is here. I added these lines at the top and bottom:
open(input + File.separator + file);saveAs("png", output + File.separator + replace(file, suffix, ".png"));
close("*");
We'll go into more detail on scripts in the future
In the meantime:
Thank you for your attention!
We will send you a survey for feedback; please take 2 minutes to answer, it helps us a lot!
